Mucogingival Surgery Definition
Mucogingival Surgery: Surgical procedures are performed to correct/eliminate anatomic, developmental, or traumatic deformities of the gingiva or alveolar mucosa.
Mucogingival Surgery Important Notes
1. Mucogingival surgeries
- Techniques of increasing the width of attached gingiva
- Free gingival graft
- Apically displaced flap
- Techniques for coverage of denuded roots
- Laterally displaced pedicle graft
- Coronally displaced flap
- Free gingival graft
- Techniques to deepen the vestibule
- Free autogenous grafts
- Techniques for removal of a frenum
2. Undisplaced flap
- It surgically removes the pocket
- It does not increase the width of the attached gingiva, instead, it decreases the width
- It is essentially an excisional procedure of the gingiva
3. Disadvantages of full-thickness flap
- Loss of facial bone height
- Not preferred in cases of fenestrations and dehiscence
Read And Learn More: Periodontics Question and Answers
Mucogingival Surgery Long Essays
Question 1. Define periodontal plastic surgery. Describe procedures available to cover denuded root surfaces.
Answer:
Periodontal plastic surgery Definition:
- Surgical procedures are performed to correct/eliminate anatomic, developmental, or traumatic deformities of the gingiva or alveolar mucosa.
Periodontal Plastic Surgery Conventional Procedures
1. Laterally displaced flap:
Recipient site:

Periodontal plastic surgery Donor site:

- Transfer the flap to the recipient site
- Suturing of flap
- Placement of periodontal pack
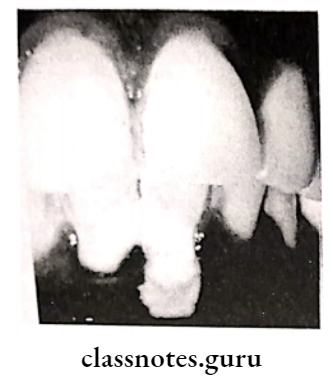
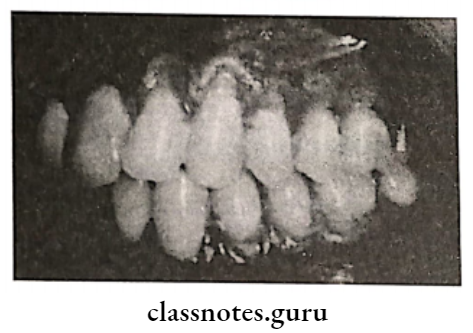
2. Double papilla flap:
By Wainberg:
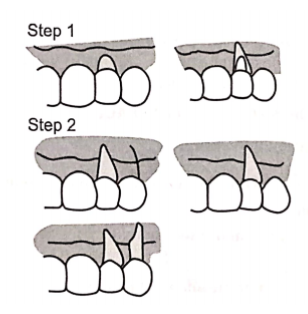
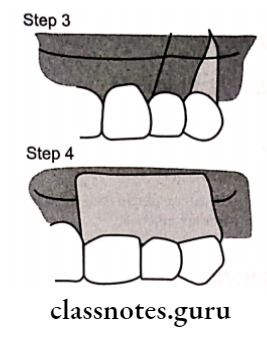
Dissecting both facial and lingual papilla
3. Coronally-repositioned flap:

Regenerative Procedures:

Mucogingival Surgery Short Essays
Question 1. Free gingival graft
Answer:
A free gingival graft is used to create a widened zone of attached gingiva
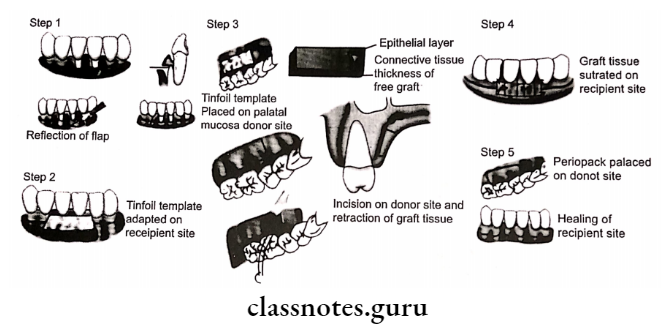
2. Variant techniques:
- Accordion technique
- Achieved by giving alternate incisions on opposite sides of the graft
- Strip technique
- Consists of 2 or 3 strips of tissue to cover the entire length of the recipient site
- Connective tissue technique
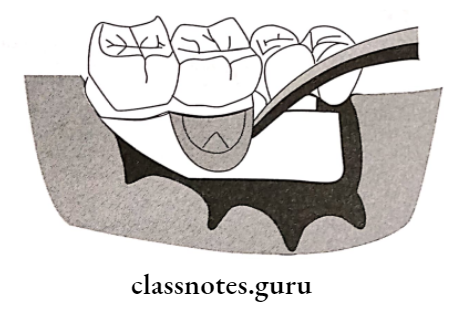
Question 2. GTR.
Answer:
After the flap surgery, epithelium from the excised margin. No need for donor site may proliferate apically
1. Classical technique of GTR:

- This results in the formation of long junctional epithelium
- Thus this should be prevented
- To prevent this, a membrane is placed between healing connective tissue and cementum
- Such a membrane is GTR (Guided Tissue Regeneration)
Types of GTR:
- Degradable- Collagen, Guidor membrane
- Non-degradable- Millipore, Teflon membrane
GTR Indications:
- Esthetic demand
- In single tooth with wide deep localized recession
- In the presence of root sensitivity
- In recession associated with class V restorations
GTR Advantages:
- No need for a donor site
- Highly esthetic
- Disadvantages:
- Technique sensitive
- Expensive
GTR Technique:
- The incision along with releasing incisions extending

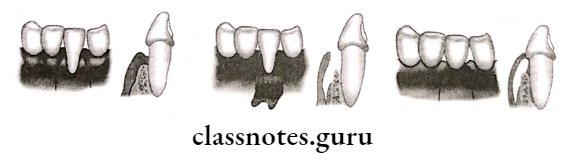
Question 3. Coronally displaced flap
Answer:
Coronally displaced flap Indications:
- Esthetic coverage of exposed roots
- Gingival recession
Coronally displaced flap Advantages:
- Treatment of multiple areas
- Adjacent teeth are safe
- The high degree of success
- It does not increase the existing problem
Coronally displaced flap Disadvantages:
- No need for two surgical procedures
Coronally displaced flap Technique:

Mucogingival Surgery Short Question And Answers
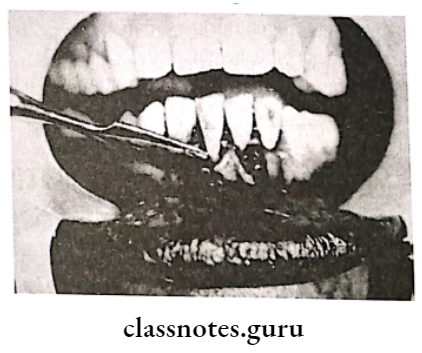
Question 1. Frenectomy.
Answer:
Frenectomy is the complete removal of the frenum including its at-attachment to the underlying bone
Frenectomy Technique:

Question 2. Mucogingival Problems.
Answer:
- Deep pockets
- Recession
- High frenal attachment
- Inadequate width of attached gingiva
Question 3. Indications of Mucogingival surgery.
Answer:
- Augmentation of the edentulous ridge
- Prevention of Residual Ridge Resorption (R)
- Crown – lengthening
- Esthetic purpose
Question 4. Frenectomy and frenotomy
Answer:
Frenectomy:
- Frenectomy is the complete removal of the frenum including attachment to the underlying bone
Frenotomy:
- Frenectomy is the relocation of the frenum usually in a more apical position
Frenectomy Indications:
- Esthetic purposes
- Deepening of vestibule in mandibular anterior area
Frenectomy Technique:

Question 5. High frenal attachment
Answer:
High frenal attachment is a condition where the frenum is. attached too close to marginal gingiva.
High frenal attachment Etiology:
- Genetic
- Gingival recession
High frenal attachment Effects:
- Tension on frenum
- Plaque accumulation
- Inhibit proper placement of toothbrush
- Poor oral hygiene
- Deep maxillary anterior vestibule
- Esthetic problems
Question 6. Vestibuloplasty.
Answer:
- It is a procedure for vestibule extension
- As described by Edlan and Mejchar
High frenal attachment Technique:
Two vertical incisions are given from the junction of marginal and attached gingiva to approx 12 mm from the alveolar margin into the vestibule
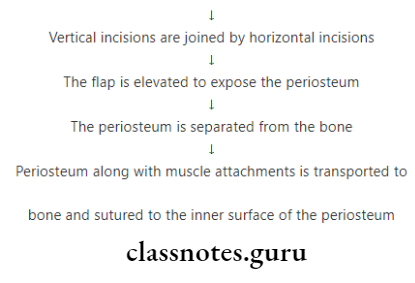
High frenal attachment Types:
- Labial vestibuloplasty
- Lingual vestibuloplasty
Question 7. Objectives of mucogingival surgery
Answer:
- Widening of attached gingiva
- Coverage of denuded roots
- Removal of an aberrant frenum
- Creation of some vestibular depth
- As an adjunct to routine pocket elimination procedure
Mucogingival Surgery Viva Voce
- Surgical removal of the frenum is indicated when tension on the frenum may tend to open the sulcus
- The ideal thickness of a free gingival autograft is 1-1.5 mm
- Revascularization of a free gingival autograft starts from 2nd or 3rd day
- The central portion of the free gingival margin is last to vascularize
- Healing of free gingival autograft of intermediate thickness of 0.75 mm is completed by 10.5 weeks
- After 24 weeks free gingival autograft placed on de- nude bone shrink by 25%
