Maxillary Sinus And Its Implications Definitions
Oroantral Fistula: Oroantral Fistula is an epithelioid, pathological, unnatural communication between the oral cavity & maxillary sinus
Maxillary Sinus And Its Implications Important Notes
1. Radiographic Features Of Maxillary Sinusitis:
- Acute Sinusitis:
- Shows uniform opacity
- Sometimes a fluid level is decreased
- Chronic Sinusitis:
- Shows pansinusitis
- Presence of fluid level
- Thickened lining membrane
- Opaque airspace may enclose polyps associated with mucosal thickening
- In the case of the presence of a tooth or root the characteristic outline is seen within the sinus
Read And Learn More: Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Question and Answers
2. Boundaries Of The Maxillary Sinus
- Roof: Formed by the floor of the orbit
- Floor: Alveolar process of maxilla
- Anterior Wall: The facial surface of the maxilla
- Posterior Wall: Sphenomaxillary wall
- Medial Wall: Lateral wall of the nasal cavity
3. Intranasal Antrostomy:
- Intranasal Antrostomy is performed to facilitate drainage at the conclusion os an operation
- To close oroantral fistula or
- To remove a tooth or root from sinus
- Surgical Procedure:
- A small-sized osteotome or gouge is pushed through the inferior meatus in the nasal cavity into the maxillary sinus
- A topical anaesthesia ointment is applied to the cotton wool which is inserted along the nasal floor adjacent to the lateral wall of the nose near the inferior turbinate
- A sharp trocar and cannula are then introduced along the floor of the nasal cavity inferior to the inferior turbinate
4. Functions Of The Maxillary Sinus:
- Humidification of inspired air
- Resonance to voice
- Lightens skull bones
- Thermal insulator
- Protects eye & cranium
Maxillary Sinus And Its Implications Long Essays
Question 1. Write a note on the anatomy of the maxillary sinus. Describe in detail about Oro antral fistula.
(or)
Define boundaries of the maxillary sinus. Describe the technique for closure of oroantral communication.
(or)
Describe the surgical anatomy of the maxillary sinus. Write a note on oroantral fistula. Antrum of High more
Answer:
Maxillary Sinus:
- Maxillary Sinus is pyramidal with a base forming the lateral nasal wall & apex at the root of the zygote.
- Capacity: 10-15 ml
- Size: Height 3.5 cm
- Width: 2.5 cm
- Anteroposterior Depth: 3.2 cm
Boundaries Of Maxillary Sinus:
- Roof: Formed by the floor of the orbit
- Floor: Alveolar process of maxilla
- Anterior Wall: Facial surface of maxilla
- Posterior Wall: Sphenomaxillary wall
- Medial Wall: Lateral wall of nasal cavity
- Vascular & Nerve Supply
- Blood Supply: Facial artery
- Infraorbital artery
- Greater palatine artery
- Nerve Supply:
- Infraorbital nerve
- Anterior, middle & posterior superior alveolar nerves
- Lymphatic Drainage: Submandibular lymph nodes
Definition Of Oro Antral Fistula:
Oro Antral Fistula is an epithelized, pathological, unnatural communication between the oral cavity & maxillary sinus
Question 2. Enumerate etiological factors of oro-antral fistula. Add a brief note on its management.
(or)
What are the causes of oro-antral communication? Describe any one method of surgical closure.
Or
Management of Oro antral fistula / Caldwellluc procedure
Answer:
Oro-Antral Fistula
Management Of Oro-Antral Fistula:
- Caldwell operation
Indications Of Oro-Antral Fistula:
- Chronic maxillary sinusitis
- Removal of foreign bodies
- Cyst & tumours
- For biopsy
- Recurrent cases
- Antral polyp
Contraindications Of Oro-Antral Fistula:
- Young age
- Acute infection
- Systemic cases
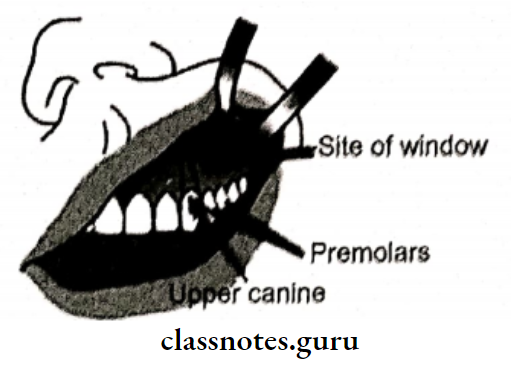
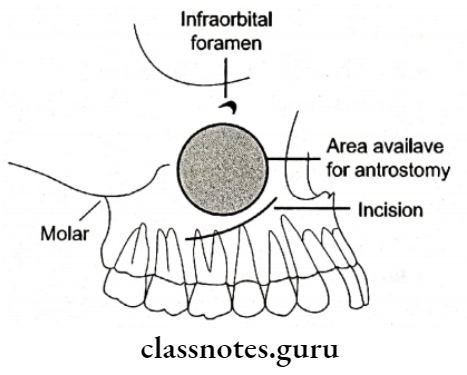
Procedure Of Oro-Antral Fistula:
- Anaesthetize
- Semilunar incision is given in mesiobuccal fold in the canine region
- Reflection of flap
- Creation of window
- Removal of sinus lining for biopsy
- Antrostomy
- Packing the sinus cavity through ribbon gauze pregnant in benzoin
- Smoothening of bony margins
- Replace the flap
- Suturing
Question 3. Write about Embryogenesis
Answer:
Embryogenesis:
- In the early stages, the maxillary sinus is high in the maxilla Later gradually grows downward by a process of pneumatization.
- The expansion of the sinuses normally ceases after the eruption of permanent teeth.
- In adults, the apices of the posterior teeth may be external to the sinus cavity.
Maxillary Sinus And Its Implications Short Essays
Question 1. Acute sinusitis.
Answer:
Etiology Of Acute Sinusitis:
- Nasal infections
- Dental infections
- Trauma
Causative Organisms Of Acute Sinusitis:
- Streptococcus
- Pneumococci
- Staphylococci
Clinical Features Of Acute Sinusitis:
- Pain on lowering your head
- Tenderness in the canine fossa
- Redness of the area
- Nasal discharge
- Nose block
- Change in voice
- Dry cough
- Fever
- Malaise
- Headache
Investigations Of Acute Sinusitis:
- The water’s view shows the haziness of antrum
- Transillumination test: opacity of sinus
- Culture: Shows organisms
Management Of Acute Sinusitis:
- Antibiotics
- Decongestants
- Analgesics
- Antihistamines
- Steam inhalation
- Local heat application
- Antral lavage
- Irrigation of sinus through lukewarm water
Complications Of Acute Sinusitis:
- Chronic sinusitis
- Osteomyelitis
- Middle ear infection
- Cellulitis
- Abscess
Maxillary Sinus And Its Implications Short Question And Answers
Question 1. Functions of the maxillary sinus
Answer:
Functions Of The Maxillary Sinus
- Humidification of inspired air
- Resonance to voice
- Lightens skull bones
- Thermal insulator
- Protects eye & cranium
Question 2. Rohrmann’s Flap.
Answer:
Rohrmann’s Flap
Rohrmann’s Flap was described by Von Rohrmann in 1936
The Procedure Of Rohrmann’s Flap:
- Injection of LA in the mesiobuccal fold
- The incision is made around the fistulous tract 3-4 mm marginal to the orifice
- Two divergent incisions are taken with blade no 15 from each side of the orifice into the buccal sulcus
- The buccal flap is advanced
- Inspect the maxillary sinus
- Arrest of haemorrhage
- Closure of wound
- Prescribe the medicines
Maxillary Sinus And Its Implications Viva Voce
- Arthroscopy is a technique by which the inside of a joint can be seen and operated on from the outside without any open surgery
- Berger’s flap for OAF closure utilizes a buccal flap
- A palatal flap has a high success rate in the management of OAF because a branch of the palatal artery is also mobilized
