Host Response – Basic Concepts Important Notes
1. Leucocytes
- Leucocytes constitute a major protective mechanism against the extension of plaque into the sulcus
- Leucocytes are attracted by plaque bacteria
2. Leukotoxin
- Leukotoxin is an exotoxin produced by A.a. contains which has a toxic effect on PMNs
- Leukotoxin enables these microorganisms to evade the host defense of phagocytosis
Read And Learn More: Periodontics Question and Answers
3. Interleukin-1-includes
- Osteoclast activating factor – causes bone resorption
- Lymphocyte activating factor – has the ability to stimulate the proliferation of T cells
- Interleukin-1 and TNF are key cytokines in the pathogenesis of periodontitis
4. Prostaglandin Ez
- The cells that produce it in periodontium are macrophages and fibroblasts
- It induces the secretion of metal matrix proteins and osteoclastic bone resorption
- Contributes to the loss of alveolar bone as seen in periodontitis
Host Response – Basic Concepts Short Essays
Question 1. Role of saliva in oral defense mechanism.
Answer:
- Swallows bacteria
- Inhibits bacterial attachment
- Bacteriocidal action
Peroxidase System:
Peroxidase (Synthesize by ductal cells)
↓
Bound to bacteria (or) Hydrogen peroxide (secreted by bacteria, neutrophils & host cells)
↓
This combines with thiocyanate secreted by ductal cells
↓Oxidation
This leads to hypothiocyanous acid
↓
Causes the death of bacteria
Lactoferrin:
Secreted by serous salivary gland
↓
Binds to iron
↓
Cut off nutrition to bacteria
↓
Results in bacteriostatic action
Lysozyme:
Secreted by mucous salivary gland
↓
Degrades cell wall
↓
Lysis of cell
Question 2. Phagocytosis.
Answer:
Phagocytes reach the site of inflammation
↓
Opsonization recognizes micro-organisms coated by Cзb
↓
Attach to them
↓
Extends pseudopodia and engulfs microorganisms
↓
Fusion of lysozymes and phagosomes occurs
↓
Resulting in phagolysosome
↓
Kill the infectious agent by following the mechanism
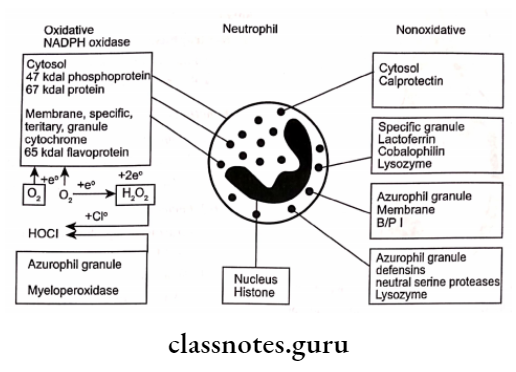
1. Oxidative:
- Stimulation of Phagocytes
- This leads to increased O2 consumption
- Formation of O2 metabolite
- Conversion of the phagocyte to superoxide anion
- Conversation to H2O2 [microbicidal]
2. Non-Oxidative:
- Granules involved
- Primary granules
- Secondary granules
- Tertiary granules
Question 3. Lymphocytes.
Answer:
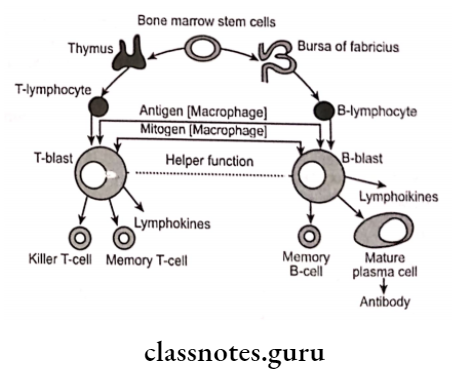
Lymphocytes Types:
1. T-cells:
- Derived from thymus
- Secrete prostaglandins
Helper T-cell (TH):
- CD4
- Releases IL2 and Interferon
- In adult periodontitis, TH increased
Suppressor T-cell (TS):
- CDa
- Releases IL4 and IL5
2. B-Cells:
- Derived from the liver, spleen, and bone marrow
- Help in humoral immunity
3. Natural Killer Cells:
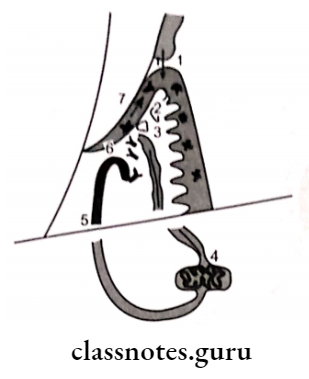
- Plaque antigens diffuse through the junctional epithelium
- Langerhans cells within the epithelium capture and process the antigens
- Antigen-presenting cells (macrophages & Langerhans cells) leave the gingiva in the lymphatics
- Antigen-presenting cells reach the lymph node and begin to stimulate lymphocytes to produce a specific immune response
- Periodontal microbe-specific antibodies are produced by plasma cells within the lymph nodes and travel back to the gingiva via blood vessels
- Antibodies leave the circulation and are carried to the crevice in the transudate from the inflamed and dilated blood vessels
- Antibody action on microbes in the crevice can result in killing, aggregation, precipitation, detoxification, opsonization, and phagocytosis of bacteria
Lymphocytes Functions:
Recognizes antigen:
Divides and provides a large no. of cells called “clonal expansion”
↓
Differentiate into
↓
Humoral responses
Different lymphocytes into plasma cells Secret es antibody
Question 4. Inflammatory cells.
Answer:
1. Neutrophils:
- The first cell of defense
- Exit circulation and reach the site
Neutrophils Functions:
- Emigration:
- Neutrophils adhere to endothelial cells
- These, then migrate across the endothelium
- Chemotaxis:
- Attracted by chemical signals from multiple sources
- Phagocytosis:
- Attaches to micro-organisms and engulfs it
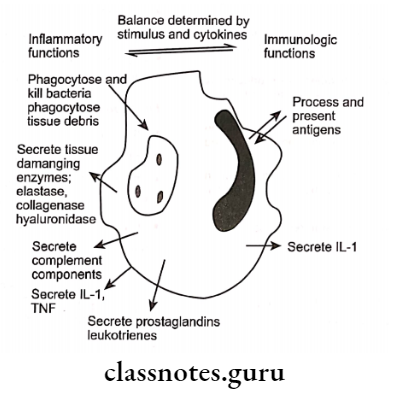
2. Macrophages:
- Develop from blood monocytes
- Migrate to the site of inflammation
- Triggered by cytokines, inflammatory mediators, and bacterial products
Macrophages Functions:
- Phagocytose kill bacteria
- Remove damaged host tissue
- Present antigens to lymphocytes
- Secretes inflammatory mediators
- Secretes tissue-damaging enzymes
- Secretes complement components
Host Response – Basic Concepts Short Answers
Question 1. Complement.
Answer:
Complement Components: C1-C9
Complement Effect: Cytolytic and cytotoxic damage to cell
Question 2. Neutrophils.
Answer:
- The first cell of defense
- Exit circulation and reach the site
Neutrophils Functions:
1. Emigration:
- Neutrophils adhere to endothelial cells
- These, then migrate across the endothelium
2. Chemotaxis:
- Attracted by chemical signals from multiple
3. Phagocytosis:
- Attaches to micro-organisms and engulfs it
Question 3. Antibacterial factors in saliva.
Answer:
- The antibacterial action of saliva is through
1. Perioxidase System:
Peroxidase (Synthesize by ductal cells)
↓
Bound to bacteria (or) Hydrogen peroxide (secreted by bacteria, neutrophils & host cells)
↓
This combines with thiocyanate created by ductal cell
↓
Oxidation
This leads to hypothiocyanous acid
↓
This leads to hypo thiocyanic acid
↓
Causes the death of bacteria
2. Lactoferrin:
Secreted by serous salivary gland
↓
Binds to iron
↓
Cut off nutrition to bacteria
↓
Results in bacteriostatic action
3. Lysozyme:
Secreted by mucous salivary gland
↓
Degrades cell wall
↓
Lysis of cell
Question 4. Any 5 Neutrophil disorders causing periodontitis.
Answer:
- Papillon Lefevre syndrome
- Down’s syndrome
- Chediak-Higashi syndrome
- Agranulocytosis
- Cyclic Neutropenia
Question 5. Functions of leukocytes
Answer:
1. Phagocytosis:
- Leukocytes engulf bacteria and foreign material
2. Chemotaxis:
- Enables leukocytes to locate their target
3. Antiallergic effect:
- Eosinophil inhibits histamine release during allergic conditions
4. Antibody formation:
- Lymphocytes are responsible for antibody formation
5. Heparin production:
- Basophils produce heparin which prevents in-intravascular clotting
6. Trephone formation:
- Leukocytes help in the formation of the telephone from plasma proteins
Question 6. Functions of IgG.
Answer:
Functions of IgG:
- Complement fixation Delayed antibody response
- Opsonization
- Cross placental barrier
- Increased concentration in GCF
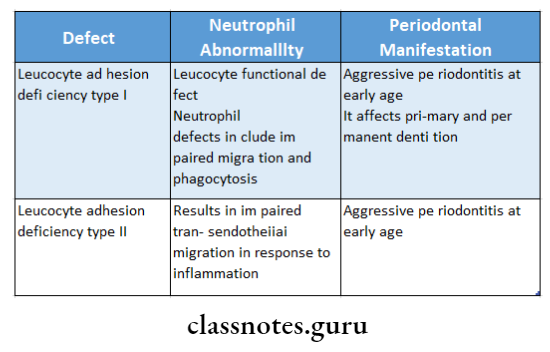
Question 7. Name functional defects of leukocytes.
Answer:
Host Response – Basic Concepts Viva Voce
- Predominant immunoglobulin in saliva is IgA
- Orogranulocytes are PMNs that reach the oral cavity
