Laboratory Procedures Before Trying Long Essays
Question 1. Define articulator. Give classification, uses, and discuss semi-adjustable articulators.
Answer:
Articulator Definition:
“A mechanical device which represents the temporomandibular joints & the jaw members to which maxillary & mandibular casts may be attached to stimulate jaw movements”.
Laboratory Procedures Before Wax Try-In
Articulator Classification:
1. Based On Theories:
- Bonwill theory articulator
- Conical theory articulator
- Spherical theory articulator
Read And Learn More: Prosthodontics Question And Answers
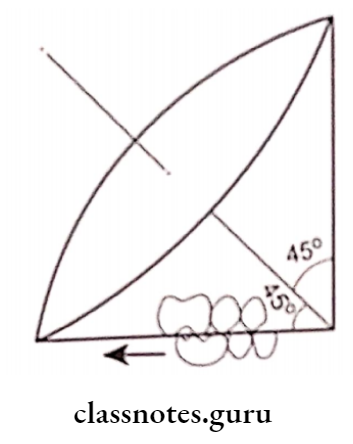
2. Based On The Type Of Occlusal Record Used:
- Interocclusal record adjustment
- Graphic record adjustment
3. Based On The Ability To Stimulate Jaw Movements:
- Class 1
- Class 2
- Class 3
- Class 4
4. Based On Adjustability:
- Nonadjustable
- Semi adjustable
- Fully adjustable
Articulator Uses:
- Diagnose the state of occlusion
- Planning of dental procedures
- Fabrication of restoration
- Correction of restoration
- Arrangement of artificial teeth
Complete Denture Wax Try-In Preparation
Semi-Adjustable Articulator:
They have adjustable horizontal condylar paths, adjustable lateral condylar paths, adjustable incisal guide tables & adjustable intercondylar distances

Types Of Articulators:
- Arcon Articulator:
- In this type condylar element is attached to the lower member of the articulator & the condylar guidance is attached to the upper member
- This resembles the TMJ.
- Advantages of Articulator: All relations are preserved even when the articulator is open or closed
- Examples: Whip mix articulator:
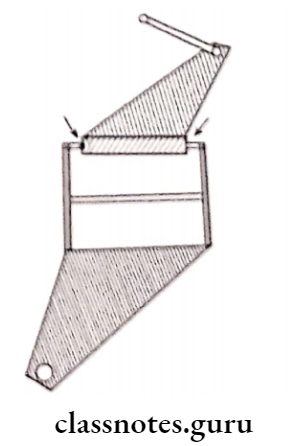
- Non-Arcon Articulator:
- This articulator has a condylar element attached to the upper member
- The condylar guidance is attached to the lower member
- It is the reverse of TMJ
- Examples: Hanau H series
Question 2. Discuss in detail the anterior teeth selection for edentulous patients. Add a note ketogenic concept.
Answer:
Anterior Teeth Selection:
Size: Methods:
- Pre-Extraction Records:
- Diagnostic cast- prepared before the extraction of teeth
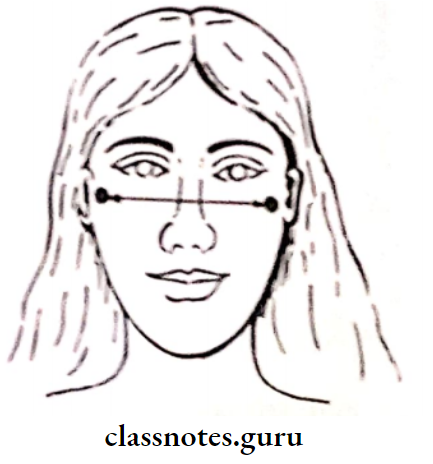
- Photographs- showing frontal and lateral views
- Radiographs- Accurate measurements not obtained
- Close relatives- If other methods fail
- Extracted teeth- Best method
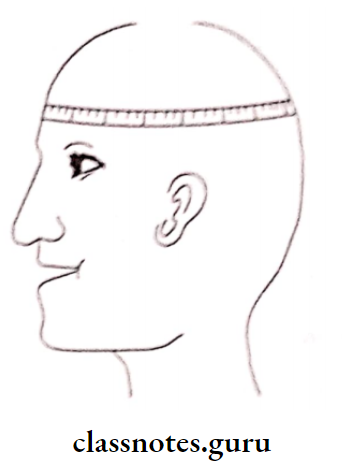
- Anthropological Measurements:
- Cephalic Index: Total width of upper anteriors= Bizygomatic width/3.36
- The total width of the lower anterior: 4/5 of the width of the upper anterior. By H. Pound
Record Base and Wax Rims in Complete Dentures
- By Sears: Width of upper central incisor, Circumference of head/13
Anatomical Landmarks:
1. Size Of Maxillary Arch:
- Distance between the incisive papilla and the hamular notch on one side.
- Distance between the two hamuli notches.
- Total width of all anterior and posterior
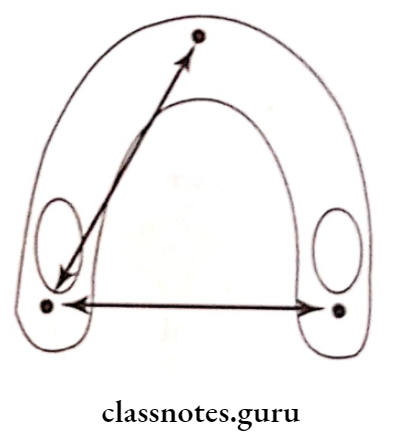
- Canine Eminence: Distance between two canine eminences combined width ofthe anterior teeth
2. Buccal Frenal Attachments: Distance between two frena = total widths of maxillary anterior
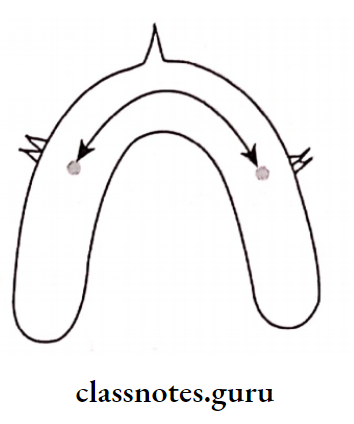
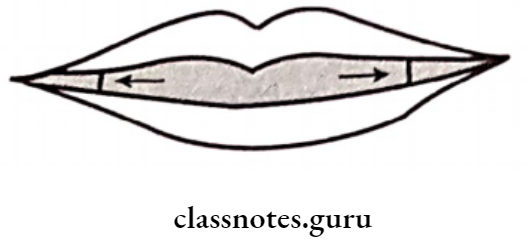
3. Corners Of The Mouth: Distance between them = total width of anterior
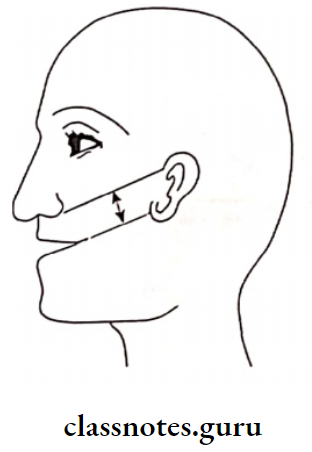
4. Theoretical Concepts:
- Winkler’s Concept:
- Physiological: Evaluate the perioral tissues and arrange the teeth
- Psychological: Camper’s line is used for it
- Raised by happy people
- Depressed downward in depressed people
- Biomechanical: Placement of teeth in the neutral zone
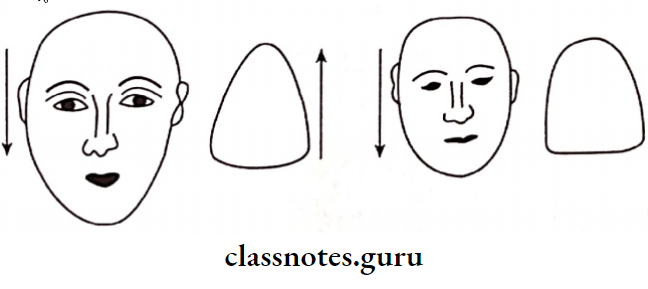
- Typal Form Theory (Leon Williams): The shape of teeth inverse the shape of the face
- Temperamental Theory:
- People based on mental, functional, and physical characteristics contain teeth
- Concept Of Harmony:
- The size of the teeth corresponds to the size of the head
5. Others:
- Size of face
- Interarch distance
- Lip length
6. Color:
- Age
- Young people have lighter teeth
- Old people – dark teeth
- More shiny
- Brownish tinge
- Habits – smokers’ porcelain teeth
- Complexion- teeth selected in harmony with the complexion
- The colour of the eyes color of iris, is considered
7. Form:
- Patient’s face (Leon William’s concept)
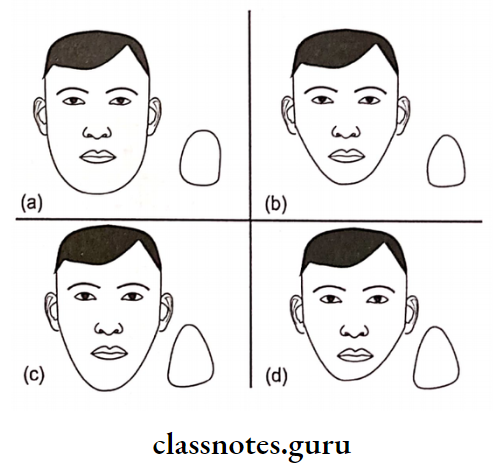
- Facial form can be ovoid, tapering, or square Teeth are selected according to it
- Form Example: Oval teeth for oval face
- (a) Square
- (b) Oval
- (c) Tapering
- (d) combination
Custom Tray Fabrication in Complete Dentures
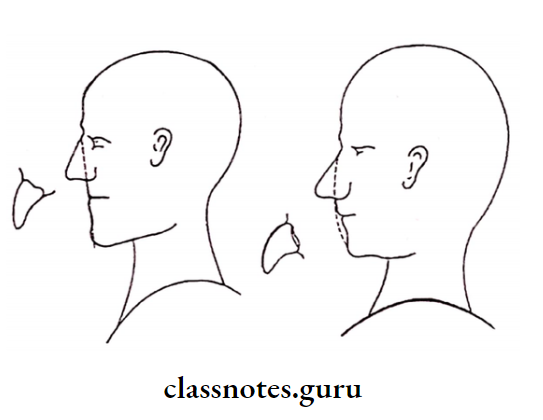
- Patient’s profile
- It can be convex, concave, or straight
- The labial form of the anterior is selected according to it
- Example: Straight labial form for straight profile
8. Dentogenic concept (SPA concept):
- Sex:
- Females: Rounded incisal edges
- Less angular teeth
- Incisal edges follow the plane of the curve of the lower lip
- Rotated distal surfaces of central
- The visible mesial third of canines
- Exposure to more interiors while smiling
- Males: More angular teeth
- Incisal edges are above the plane of occlusion
- The mesial end of the laterals is hidden by the central
- The middle 2/3rd of the canine is visible
- Prominent cervical regions
- Females: Rounded incisal edges
- Personality:
- Squarish-vigorous people
- Flat: Executives
- Age:
- Increased horizontal overlapping of posteriors
- Reduced interarch distance
- Reproduce abrasion and gingival recession in teeth as present in an old individual
Question 3.Given its functions and requirements of an articulator.
Or
Requirements of the articulator
Answer:
Functions Of Articulator :
- Holds maxillary and mandibular casts in a determined fixed relationship
- Stimulates jaw movements like opening and closing
- Produces border and intraborder movements of the teeth similar to those in the mouth
Requirements of Articulator: Requirements of Articulator
- Minimal Requirements:
- The articulator should hold casts in the correct horizontal relationship
- The articulatorshould hold casts in the correct vertical relationship
- The casts should be easily removable and re-attachable
- The articulator should provide a positive anterior vertical stop
- The articulator should accept the face bow transfer record using an anterior reference point
- Articulator should open and close in a hinge movement
- Articulator should be made of non-corrosive and rigid materials that resist wear and tear
- Articulator should not be bulky or heavy
- There should be adequate space present between upper and lower members
- The moving parts should move freely without any friction
- The nonmoving parts should be of a rigid construction
- Additional Requirements:
- Condylar guides should allow protrusive and lateral jaw motion
- The condylar guide should be adjustable in a horizontal direction
- The articulator should be adjustable to accept and alter
- Bennett movement
- The incisal guide table should be customized
Question 4. Selection of posterior teeth in complete denture
Or
Criteria For Posterior Teeth Selection
Or
Posterior Teeth Selection
Answer:
Posterior Teeth Size:
- Buccolingual Width: Such that it
- Provide escape of food
- Neutralizes forces from cheeks
- Prevent cheek biting
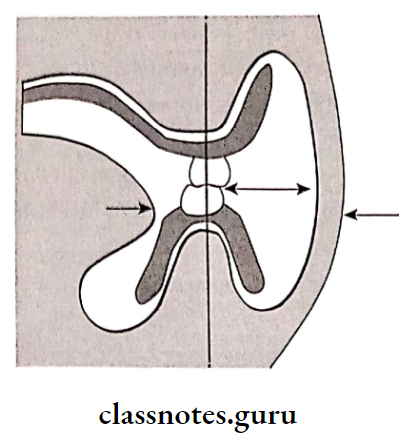
- Mesiodistal length: Such that
- The combined length of all posteriors doesn’t exceed the distance between canine and retromolar pad
- Occlusogingival height
- The occlusal plane should be at the midpoint of the interocclusal distance
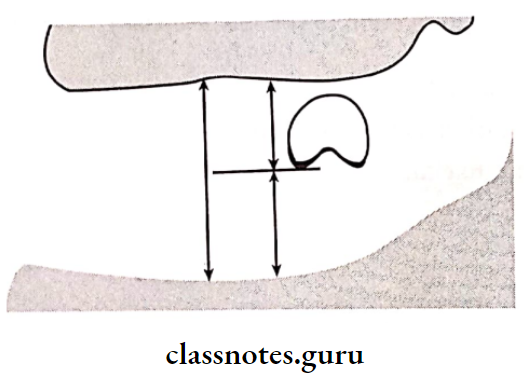
Steps Before Wax Try-In in Prosthodontics
2. Form:
- High cuspal height for steep condylar guidance
- Shallow cusps for shallow ridge
- Monoplane teeth for posterior crossbite