Impression And Mouth Preparation Long Essays
Question 1. Define impression. Discuss in detail the most widely accepted technique of making an impression in complete dentures.
Answer:
Impression:
A complete denture impression is a negative registration of the entire denture-bearing, stabilizing & border seal areas present in the edentulous mouth.
Impression Techniques:
- Mucostatic
- Mucocompressive
- Selective pressure technique
- It is the most widely accepted impression technique
- In this technique, forces are confined to stress-bearing areas, whereas non-stress-bearing areas are relieved
Read And Learn More: Prosthodontics Questions And Answers
Impression Technique:
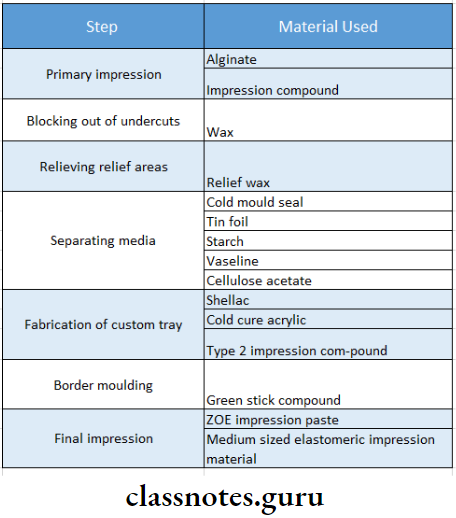
- The primary impression is made with overextended borders. The primary cast is prepared from it
- Undercuts are blocked with wax on the cast. Relief wax is applied over relief areas on the cast
- A spacer is adapted throughout the extent of the special tray
- Separating media like cold mold seal or tin foil is applied overcast
- A special tray with a handle is fabricated
- Impression should be 2 mm short of the sulcus
- Materials used for it are: Shellac, cold-cure acrylic, Type II impression compound
- The wax spacer is then scraped off
- Border molding is done using greenstick compound
- Relief wax is removed
- Escape holes are made over the tray
- Secondary impression material is loaded over the tray
- Impression is then seated in the patient’s mouth, and the secondary impression is made.
Impression and Mouth Preparation in Complete Dentures
Impression Materials Used:
Question 2. Define impression.
Or
Discuss various impression procedures in the complete denture.
Or
Add a note on the selection of impression materials.
Answer:
Impression:
A complete denture impression is a negative registration of the entire denture-bearing, stabilizing & border seal areas present in the edentulous mouth.

Impression Selection Of Materials:
- Impression should be fluid enough to adapt to oral tissues
- Impression should be viscous enough to be contained in the tray that is seated in the mouth
- While in the mouth, they should set into a rubbery or rigid solid in a reasonable amount of time
- The set impression should not tear or distort when removed
- The impression made should be dimensionally stable
- Stability should be maintained after the removal of a cast so that a second or third cast can be made
- The material should be biocompatible
- Impression should be cost-effective
- Should be nontoxic
- Impression should be acceptable to patients with a pleasant odor and color
- Should have adequate shelf life, Easy to use with minimum equipment, should have adequate strength
Complete Denture Pre-Prosthetic Preparation
Question 3. Define retention, stability, and support in the complete denture. Discuss various factors affecting retention.
Or
Define complete denture retention. Enumerate various factors of retention.
Or
Write in detail about retention in complete dentures.
Answer:
- Retention: That quality inherent in the prosthesis that resists the force of gravity, adhesiveness of foods, and the forces associated with the opening of the jaws
- Stability: The quality of the denture to be firm, steady, and constant, to resist displacement by functional stresses & not to be subject to change of position when forces are applied
- Support: Resistance to vertical forces of mastication, occlusal forces, and other forces applied in a direction toward the denture-bearing area
Factors Affecting Retention:
1. Anatomical Factors:
- Size Of Denture Bearing Area:
- The retention increases with an increase in the size of the denture-bearing area
- Maxillary dentures are more retentive than mandibular as it has 24 cm2 compared to that 14 cm2
- Quality Of Denture Bearing Area:
- Displaceability of the tissues influences the retention of dentures
- Displacement of tissues during impression-making
- Result in tissue rebounding
- This leads to a loss of retention of dentures
2. Physiological factors:
- Saliva:
- Thick & ropy saliva-loss of retention
- Thin & watery saliva- compromised retention
- Ptyalism- gagging
- Xerostomia-Soreness & irritation
3. Physical factors:
- Adhesion:
- The physical attraction of unlike molecules to one another
- The amount of adhesion present is proportional to the denture base area
- In xerostomia there is no adhesion
- Cohesion:
- The physical attraction of like molecules for each other
- Act within the film of saliva
- Watery serous saliva- more retentive
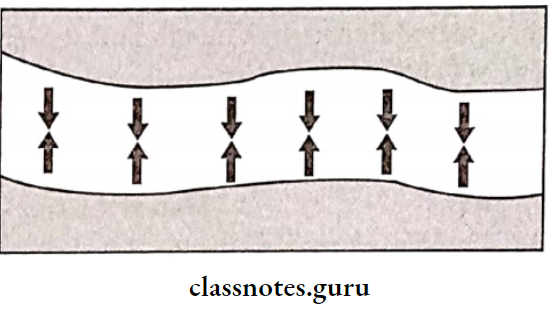
- Interfacial Surface Tension:
- The tension or resistance to separation possessed by the film of liquid between two well-adapted surfaces
- Present within the film of thin saliva
- Useful in the retention of the maxillary denture
- Depends on the presence of air at the margins of liquid & solid contact

- To attain maximum interfacial tension
- Saliva should be thin
- Perfect adaptation
- Covering a large denture area
- The presence of good cohesive and adhesive forces
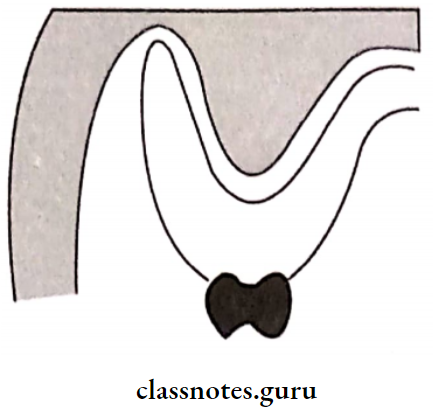
- Capillarity Attraction:
- That quality or state, because of surface tension, causes elevation or depression of the surface of a liquid that is in contact with a solid
- The presence of close adaptation between the denture and the mucosa increases surface contact
- Results in an increase in retention
- Capillarity Attraction Factors:
- Close adaptation
- Greater surface area
- A thin film of saliva
Impression Techniques in Prosthodontics
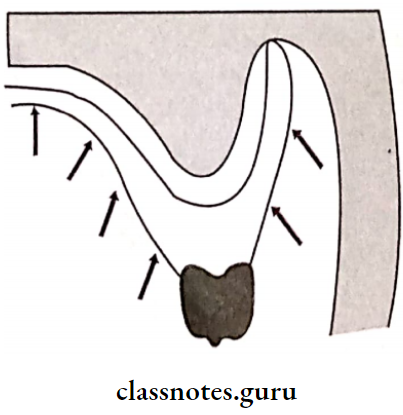
- Atmospheric Pressure And Peripheral Seal:
- Atmospheric Pressure And Peripheral Seal prevent air entry between the denture and soft tissue
- To obtain it denture borders should rest on soft and resilient tissues
- On application of forces, a vacuum is created that aids in retention
- This is a natural suction of the denture
- Atmospheric Pressure and Peripheral Seal are directly proportional to the denture base area
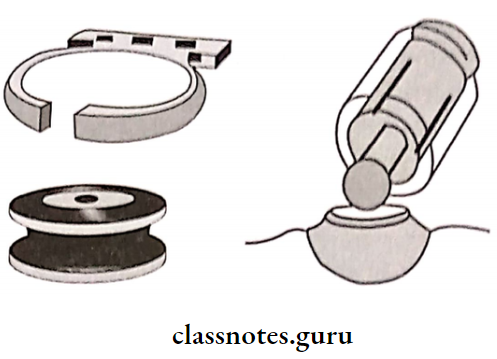
4. Mechanical Factors:
- Undercuts
- Retentive springs
- Magnetic forces
- Denture adhesives
- Suction chambers and suction discs
5. Muscular Factors:
- The balance should be between the forces acting from the buccal musculature and the tongue
Question 4. Define complete denture impression. Discuss impression theories and techniques in treating complete denture patients.
Answer:
Complete Denture Impression:
A complete denture impression is a negative registration of the entire denture-bearing, stabilizing, and border seal areas present in the edentulous mouth.

Techniques Of Impression:
Mouth Preparation Before Complete Dentures
1. Custom Tray Impression:
- Design a custom tray with a spacer
- It should be 2 mm short of the sulcus
- Border molding is done
- It results in recording the sulcus in dynamic function
- Spacer is scraped
- The impression is recorded by ZOE
- It results in recording the stress-bearing areas under pressure, and the non-stress-bearing areas are relieved
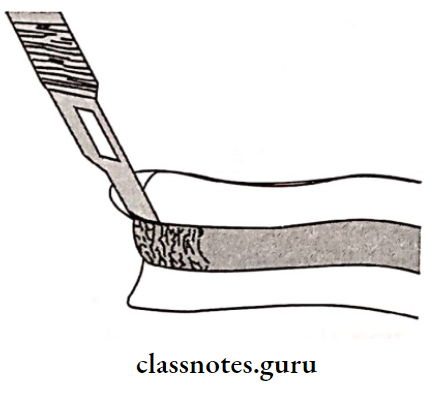
2. Tray Compound:
- The impression made using the tray impression compound
- The impression is refined and trimmed
- The metal wire is attached to the tray compound to act as a handle
- Treat it as a custom tray
- Border moulding done
- Wash the impression made on it
Question 5. Define impression. Discuss biological considerations for a maxillary impression.
Answer:
Complete Denture Impression:
A complete denture impression is a negative registration of the entire denture-bearing, stabilizing, and border seal areas present in the edentulous mouth.
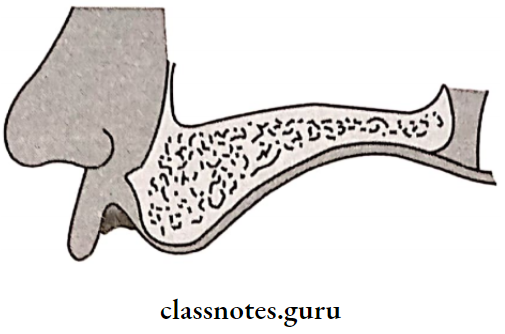
Biological Considerations Of Maxillary Impression :
- The anatomy of the edentulous ridge in the maxilla is important in designing a complete denture
- Some parts of the ridge are capable of withstanding forces compared to others
- Thus, it is considered before impression-making
Impression Limiting Structures:
- Labial Frenum:
- Labial Frenum is the limiting structure of the Maxilla and Mandible
- Labial Frenum is a fibrous band
- Covered by a mucous membrane
- Extension: Labial aspect of the residual ridge to the lip
- Maxillary: Passive due to the absence of muscle fibers
Recorded In Impression:
Recorded in impression as a V-shaped notch
- Requirement: Notch should be narrow and deep
- Labial Vestibule:
- That portion of the oral cavity which is bounded on one side by the teeth, gingival, and alveolar ridge and on the other side by the lips and cheeks
- Presence of orbicularis oris
- Labial Vestibule has an indirect displacing effect on the denture
- Buccal Frenum:
- Buccal Frenum separates the labial and buccal vestibule
- Muscle attachments present: Levator anguli oris, orbicularis oris, and buccinator
- Buccal Frenum needs greater clearance on the buccal flange of the denture
- Buccal Vestibule:
- Buccal Vestibule extends from the buccal frenum to the hamular notch
- Its size varies with: the contraction of muscle, the position of mandible and amount of bone loss in the maxilla
- Hamular Notch:
- Depression present between maxillary tuberosity and hamulus of medial pterygoid plate
- Can be easily displaced to achieve posterior pala tal seal
Impression Supporting Structures:
1. Primary Stress Bearing Areas:
- Hard Palate:
- Trabeculae pattern of it perpendicular to the direction of forces acting on it
- Thus it acts as a primary stress-bearing area
- Postero-Lateral Slopes Of Residual Ridge:
- Ridge rapidly resorbs following extraction of teeth
- Resilient submucosa over provides support to the denture
2. Secondary Stress Bearing Areas:
- Rugae:
- Rugae is a secondary support area in Maxilla
- Rugae is covered by a thin mucosa
- Rugae Location:
- In the anterior region of the palatal mucosa
- At the angle of the occlusal plane of the residual ridge
- Rugae Significance: Important in speech
- Precautions During Fabrication:
- Should not distort this area while impression-making
- Metal dentures should reproduce this area to make it comfortable
- Rugae Location:
- Maxillary Tuberosity:
- Bulbous extension of residual alveolar ridge in 2nd 3rd molar region
- It is least likely to resorb
Secondary Stress Relief Areas:
- Incisive papilla
- Relief Areas Location:
- Midline behind central incisors
- Reason For Relieving:
- The reason For Relieving is the exit point of nasopalatine nerves and vessels
- If it is not relieved it compresses vessels and nerves
- Reason For Relieving Results:
- Necrosis of the area
- Paraesthesia of the anterior palate
1. Cuspid Eminence:
- Bony elevation on residual alveolar ridge
- Location: between canine and 1st premolar

2. Mid-Palatine Raphe:
- Median suture area
- As it is covered by thin mucosa, it should be relieved
3. Fovea Palatine:
- Coalescence of ducts of mucous glands
- Determines the position of the posterior border of the denture
- Relieved because of the presence of ducts
Question 6. Describe mandibular anatomical structures.
Answer:
Limiting Structures:
- Labial Frenum:
- Active due to the presence of muscle incisive and orbicularis oris
- It is a fibrous band
- Covered by mucous membrane
- Extention: labial aspect of the residual ridge to lip
- Recorded In Impression: Recorded in impression as a V-shaped notch
- Requirement: Notch should be narrow and deep
- Labial Vestibule:
- That portion of the oral cavity which is bounded on one side by the teeth, gingiva, and alveolar ridge and on the other side by the lips and cheeks
- Influences retention of dentures
- Buccal Frenum:
- Contains fibers of the buccinator
- Prevent displacement of denture
Buccal Vestibule:
- Extends from buccal frenum to retromolar region
- Bound by alveolar ridge and buccinator
- Influenced by masseter
- Notch is produced in denture flange called masseteric notch
- Lingual Frenum:
- Effects stability of denture high frenal attachment is called tongue tie
Alveololingual Sulcus:
- Has 3 Regions:
- Anterior Region
- From lingual frenum to pre-mylohyoid fossa
- Middle Region
- From the pre-mylohyoid fossa to the distal part of the mylohyoid ridge
- Posterior Region
- In the region of retro mylohyoid fossa
- Determines lateral throat form
- Anterior Region
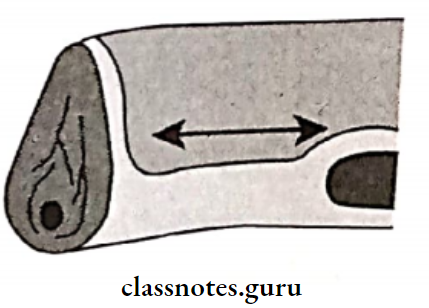
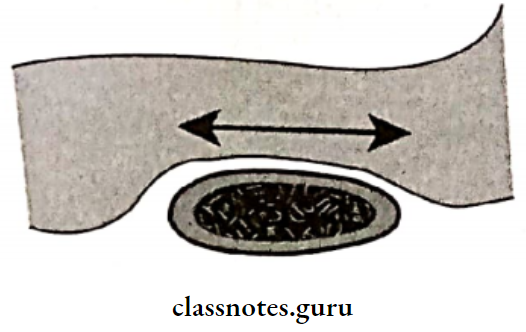
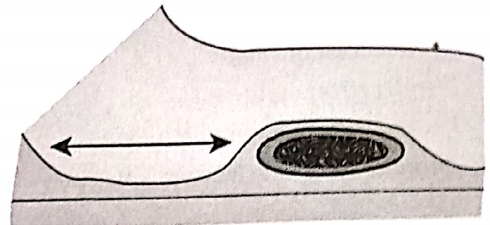
- Retromolar Pad:
- Forms posterior seal of denture
- Location: Distal to the third molar
- Consists of: Loose connective tissues, mucosal glands
- Retromolar Pad Boundaries:
- Posteriorly: temporalis
- Lateral: buccinator
- Medial: Pterygomandibular raphe and superior constrictor
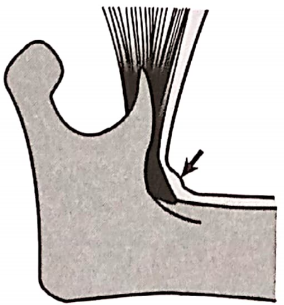
- Pterygomandibular Raphe:
- Extend: Hamular process to the mylohyoid ridge
- Muscles Attached:
- Postero- medially- superior constrictor
- Antero-laterally-buccinator

Alveololingual Sulcus Supporting Structures:
1. Buccal Shelf Area:
- Between the buccal frenum and anterior border of the masseter
- Buccal Shelf Area Boundaries:
- Medial: crest of the ridge
- Distal: retromolar pad
- Lateral: external oblique ridge
- Buccal Shelf Area Significance: Width increases with resorption of the ridge
- Serves as primary stress-bearing area
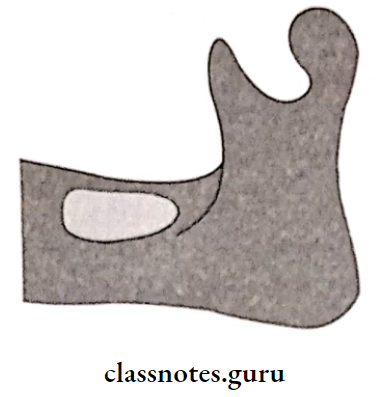
2. Residual Alveolar Ridge:
- Flat with concave denture-bearing surface
- On resorption inclines outward
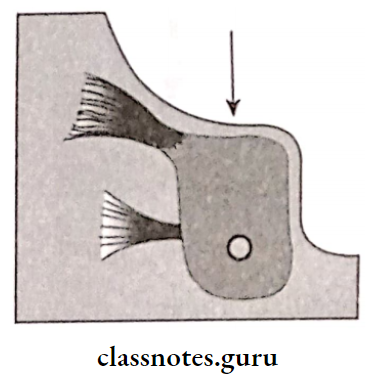
Relief Areas Mylohyoid Ridge:
- Lies close to the inferior border of the mandible
- Covered with mucosa so should be relieved
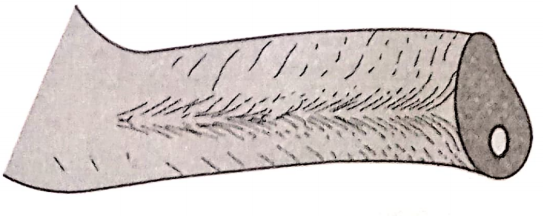
3. Mental Foramen:
- Location: Between 1st & 2nd premolar region
- Relieved as it may lead to paraesthesia
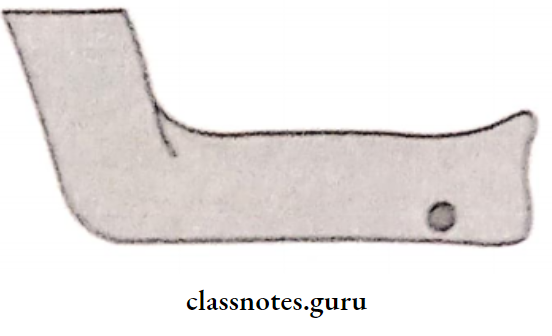
4. Genial Tubercle:
- Location: anterior on the lingual side of the body of the mandible
- Increases due to resorption
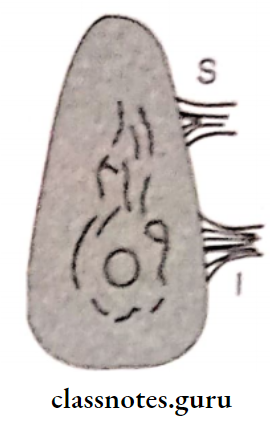
5. Torus Mandibularis:
- Location: on lingual side near premolar region (b)
- Covered by a thin mucosa
- Relieved or surgically removed
Question 7. Discuss principles and objectives of making impressions for completely edentulous patients.
Or
What are the objectives of impression-making
Answer:
Principles Of Impression Making:
- Presence of healthy oral tissues
- Inclusion of all supporting and limiting tissues
- Borders within anatomical and physiological limitations
- Border molding – physiological type
- Space between material and tray
- Not damaging the tissues
- Application of selective pressure technique
- Use of guiding mechanism
- Use of dimensionally stable materials
- Similarity to the form of dentures
Objectives Of Impression Making:
1. Retention:
“That quality inherent in the prosthesis which resists the force of gravity, adhesiveness of foods, and the forces associated with the opening of the jaws”.
- Retention Factors:
- Anatomical Factors:
- Size of denture-bearing area
- Quality of denture-bearing area
- Physiological Factors:
- Saliva
- Physical Factors:
- Adhesion
- Cohesion
- Interfacial surface tension
- Capillary attraction
- Atmospheric pressure
- Mechanical Factors:
- Undercuts
- Retentive springs
- Magnetic forces
- Denture adhesives
- Suction chambers and suction discs
- Muscular Factors:
- Anatomical Factors:
- The balance should be between the forces acting from the buccal musculature and tongue
2. Stability:
- The quality of the denture to be firm, steady, and constant, to resist displacement by functional stresses and not to be subject to change of position when forces are applied
- Stability withstands horizontal forces
- Stability Factors:
- The vertical height of the residual ridge
- Quality of soft tissue
- Quality of impression
- Occlusal rims
- Teeth arrangement
- Shape of denture
- Stability Factors:
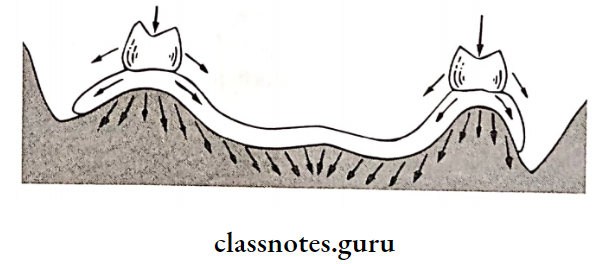
3. Support:
- Resistance to vertical forces of mastication, occlusal forces and other forces applied in a direction toward the denture-bearing area
- The denture base should cover as much denture-bearing area as possible
- Results in the distribution of forces over a wider area
- This leads to a reduction of force per unit area
Called Snow Shoe Effect:
4. Aesthetics:
- Thicker flange leads to fullness of the mouth
5. Preservation of Remaining Structures:
- Muller stated that the preservation of what remains is more important rather than to replace what is lost.
- Stress is provided over the stress-bearing area.
- Relief is provided over non-stress-bearing areas.
- Prevent damage to oral structures.
- Avoid overextension of dentures.
Question 8. Define stability and discuss factors affecting it.
Answer:
Stability:
- “The quality of denture to be firm, steady and constant, to resist displacement by functional stresses and not to be subject to change of position when forces are applied”.
- Stability withstands horizontal forces
Stability Factors:
1. Vertical Height Of Residual Ridge:
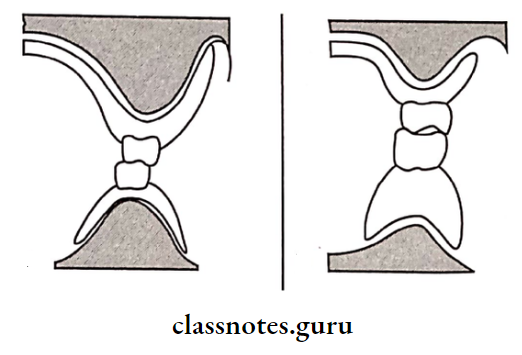
- A ridge with an adequate height of ridge provides sufficient support
- Resorbed ridge causes loss of stability or reduced stability of the denture
Full Denture Clinical Steps – Impression and Prep
2. Quality Of Soft Tissue:
- Adequate submucosa is required for good stability
- Excessive submucosa results in poor stability
3. QualitOf Impression:
- The Impression Should Be:
- Accurate
- Smooth surface
- Devoid of voids
- Not wrap on removal, Dimensionally stable
4. Occlusal Plane:
- Should be parallel to the ridge
- Should divide interarch space equally
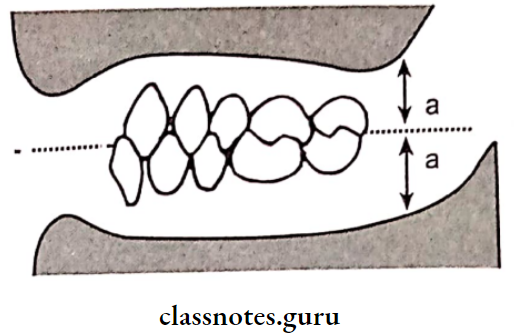
5. Teeth Arrangement:
- Teeth are arranged in a neutral zone
- That is balance is achieved between tongue and buccal musculature
6. Shape Of Denture:
- The polished surface should resemble oral structures
- Should not interfere with the functioning of oral structures
