Impression And Mouth Preparation Definitions

Impression And Mouth Preparation Important Notes
1. Types Of Impression:
- Muco compressive – records tissue in functional and displaced form
- Mucostatic records tissue in a relaxed form
- Selective pressure – records tissue without interfering with the limiting structures at function and rest
Read And Learn More: Prosthodontics Question And Answers
2. Objectives Of Impression:
- Retention: It is the resistance to displacement away from the tissue surface. It is a mucosa-borne phenomenon.
- Support: It is the resistance to the occlusal forces in the vertical direction. It is a bone-borne phenomenon.
- Stability: It is resistant to lateral shifting.
- Preservation of remaining structures.
Mouth Preparation in Complete Dentures
3. Factors Affecting Retention:
- Anatomical factors- Size of denture bearing area, quality of denture bearing area
- Physiological factor – Saliva Physical factor-adhesion, cohesion, capillary attraction, interfacial surface tension, atmospheric pressure
- Mechanical factors- Undercuts, retentive springs, magnetic forces, denture adhesives
- Muscular factors
4. Primary Stress-Bearing Areas:
5. Secondary Stress-Bearing Areas:
6. Relief Areas:
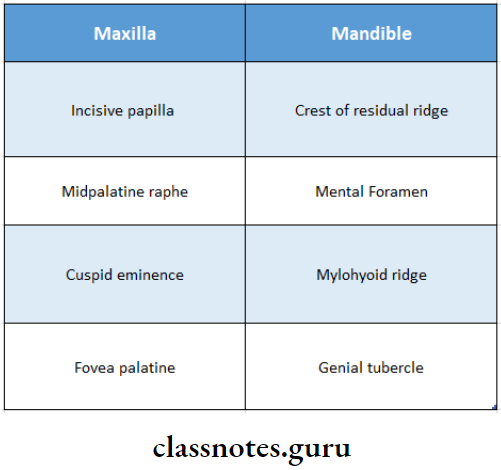
7. Anterior Vibrating Line:
- Anterior Vibrating Line is an imaginary line at the junction of the attached tissues overlying the hard palate and movable tissues of the soft palate
- The Anterior Vibrating Line is always on soft palatal tissue
- The Anterior Vibrating Line is visualized by asking the patient to say “ah” with a short, vigorous burst
Pre-Prosthetic Surgery for Complete Dentures
8. Posterior Vibrating Line:
- Posterior Vibrating Line is an imaginary line at the junction of the aponeurosis of the tensor veli palatini and a muscular portion of the soft palate
- Posterior Vibrating Line represents the demarcation between the parts of the soft palate showing limited movements and those with marked movements
- Posterior Vibrating Line is the most distal extension of the denture
9. Alveolar Lingual Sulcus:
- Extends from the lingual frenum to the retro mylohyoid curtain
- It is divided into three parts
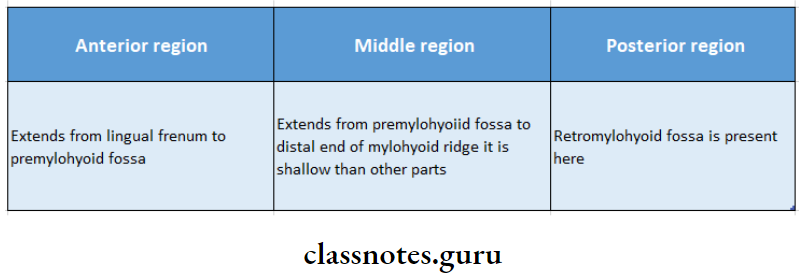
10. Posterior Palatal Seal:
- Lies between the anterior and posterior vibrating line
- Functions
- Retention of the maxillary denture
- Maintain contact with the anterior portion of the soft palate during functional movements
- Slightly displaces the soft tissue at the distal end of the denture to ensure a complete seal that helps in the retention of the denture.
- Prevents the ingress of food and saliva beneath the denture base.
- Prevents excess impression material from running down the patient’s throat.
11. Buccal Frenum:
- The buccal frenum of maxilla contains Caninus or levator anguli oris.
- The buccal frenum of mandible contains Triangularis or depressor anguli oris.
12. Pterygomandibular Raphe:
- Pterygomandibular Raphe is the tendinous insertion of the superior constrictors and buccinators
- Pterygomandibular Raphe arises from the hamular process of the medial pterygoid
- Gets attached to the mylohyoid ridge
13. Fovea Palatine:
- The fovea palatine is are indentations near the midline of the palate formed by the coalescence of several mucous gland ducts.
- The fovea palatine is always on the soft palate, 2mm behind the vibrating line.
14. Retromylohyoid Fossa Is Bounded By:
- Anterior – Retro mylohyoid curtain
- Posterolateral – Superior constrictor of the pharynx
- Posteromedial – Palatoglossus and lateral surface of the tongue
- Inferior- Submandibular gland
15. Buccal Frenum Has The Following Muscle Attachments:
- Levator anguli oris
- Orbicularis oris
- Buccinator
16. Buccal Shelf Area Is Bounded By:
- Medial crest of the ridge
- Distally-retromolar pad
- Laterally external oblique ridge
Complete Denture Mouth Preparation Steps
17. Retromolar Pad:
- Contains glandular tissue and fibers of the temporalis, buccinators, superior constrictor, and pterygomandibular raphe
- All these prevent the placement of extra pressure
- Functions
- Provides a peripheral seal to the mandibular denture
- Marks distal extension
- Provides retention, stability, and support to the denture
18. Frena Present:
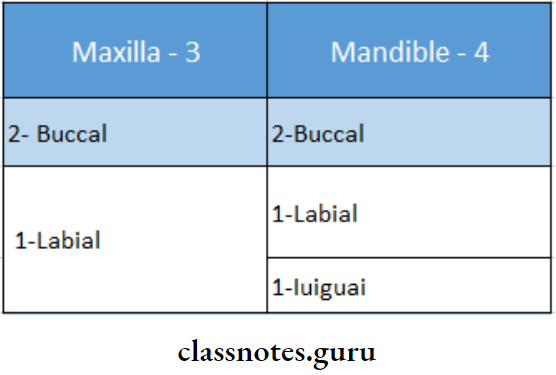
19. Border Molding:
- Border molding is the procedure by which the entire periphery of the tray is refined
- Polyether impression material is the material of choice
- Ideal requisites
- Should have sufficient viscosity
- Should not be sticky
- Should have a setting time of 3-5 min
- Should not displace tissues
- Should be easily trimmed
- Should retain its flow properties
20. Advantages Of ZOE Paste Include:
- Accurate borders are formed since the material is more plastic in nature.
- Does not absorb the mucous secretion produced in the palate and thus accurately records the palatal part of the impression.
- Does not require a separating medium.
21. Modiolus Is A Point Where Eight Muscles Meet At The Angle Mouth:
- Depressor anguli oris (or) tringularis
- Levator anguli oris or canines
- Risorius
- Orbicularis oris
- Buccinators
- Zygomaticus major
- Quadratus labii superioris
- Quadratus labii inferioris
22. Snow Shoe Effect:
- The denture base should cover as much denture-bearing area as possible
- It results in the distribution of forces over a wider area
- Leading to the reduction of force per unit area
- Called the snowshoe effect
Prosthodontics Mouth Preparation Guide
Impression And Mouth Preparation Short Essays
Question 1. Pre-prosthetic surgical management in complete denture
(or)
Pre-prosthetic surgery
Answer:

Question 2. Mucostatic impression.
Answer:
Mucostatic Impression:
- Mucostatic impression is an impression technique used in complete denture patients based on the theory of impression-making.
- By Richardson
- The impression is made with the oral mucous membrane & the jaws in a normal, relaxed condition
- The material Of Choice is impression plaster
- Border molding is not done here
- Tray Used: Oversized tray
- Retention: Due to interfacial surface tension
Significance Of Mucostatic Impression:
- Closely adapted denture
- Good stability of the denture
Disadvantages Of Mucostatic Impression:
- Poor peripheral seal
- Poor retention
- Mucostatic Synonym: Passive impression, as the impression is made in the rest position of oral tissues
Question 3. Posterior palatal seal area
Or
Definition and functions of the posterior palatal seal.
Answer:
Posterior Palatal Seal Definition:
The soft tissues at or along the junction of the hard & soft palates, on which pressure within the physiological limits of the tissues can be applied by a denture to aid in the retention of the denture
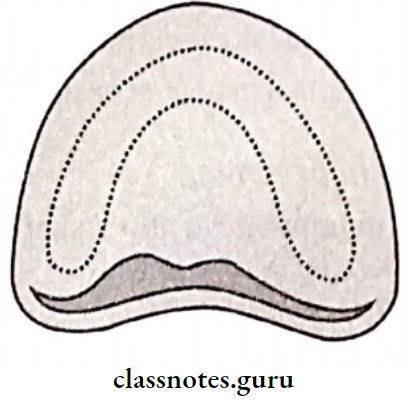
- Functions Of Posterior Palatal Seal:
- Aids in retention
- Maintain constant contact with the soft palate during functions
- Reduces gag reflex
- Prevents the formation of a gap between the denture and palate during the function
- Prevents food accumulation
- Compensate for polymerization shrinkage
- Parts Of Posterior Palatal Seal:
- Pterygomaxillary seal
- Postpalatal seal
Methods To Record It:
- Conventional approach
- Fluid wax technique
- Arbitrary scraping of the master cast
- Extended palatal technique
Question 4. Methods of recording the posterior palatal seal
Answer:
1. Conventional Method
Fabricate a trial base using a shellac base plate or self-cure resin
- The posterior palatal area is wiped with gauze
- T burnisher is used to locate the hamular notch by palpating posterior to the maxillary tuberosity on both sides
- The full extent of the hamular notch is marked with a delible pencil
- The posterior vibrating line is marked
- The line marked in the hamular notch is connected with a posterior vibrating line
- The trial base is inserted into the patient’s mouth
- Markings are transferred to the trial base is seated on the master cast
- This transfers the markings to the cast
- The trial base is trimmed to the posterior border Anterior vibrating line is marked in the patient’s mouth
- These markings are transferred to the cast. The area between the anterior and posterior vibrating line is scraped
Oral Preparation Before Complete Dentures
2. Fluid Wax technique:
- Wash impression is made
- Anterior and posterior vibratory lines are marked in the patient’s mouth
- The impression is re-inserted in the patient’s mouth
- Markings are transferred into the impression. The impression is painted with wax in the area of markings
- The impression tray is inserted in the patient’s mouth, and the patient is asked to make rotational movements
- The impression is removed after 4-6 minutes and examined
- In contrast to the green stick compound, glossy areas show tissue contact
- The procedure is repeated till even tissue contact is achieved
- Wax in the region of the anterior vibrating line should have a knife-edge margin
3. Arbitrary Scrapping Of Master Cast:
- In this technique, anterior and posterior vibratory lines are visualized in the patient’s mouth and ap- approximately marked overcast
- The technician scrapes 0.5-1 mm of stone in the posterior palatal seal area and fabricates the denture
