Gastrointestinal Important Notes
1. Drugs used in peptic ulcer
2. Cimetidine
- Inhibits several cytochrome P-450 isoenzyme
- Reduces hepatic blood flow
- Inhibits the metabolism of many drugs
Gastrointestinal system questions and answers
Read And Learn More: Pharmacology Question and Answers
3. Kaolin
- It is a hydrated aluminum silicate
- Used in the treatment of diarrhea
- Act as an absorbent of bacteria and bacterial toxin
4. Antacids
- They are salts of magnesium, calcium, and aluminum
- Produces laxatives or constipating effects
5. H2 receptor antagonist
- They are ranitidine, cimetidine, famotidine
- Inhibit gastric secretion
- Adverse effects
- Gynaecomastia
- Impotence
6. Omeprazole
- Inhibits proton pump
- It is powerful
- Totally abolishes HC1 secretion
7. Drugs used in motion sickness
- Scopolamines
- Antihistamines
Gastrointestinal Long Essays
Question 1. What is an antacid? Classify with suitable examples. Mention the merits and demerits of NaHC03 as an antacid.
Answer:
Antacids
- Antacids are basic substances that neutralize gastric acid and raise the pH of gastric contents
Antacids Classification
1. Systemic antacids
- Sodium bicarbonate
- Sodium citrate
2. Non-systemic antacids
- Magnesium hydroxide
- Magnesium trisilicate
- Aluminum hydroxide gel
- Magaldrate
Sodium Bicarbonate as Antacids:
Sodium Bicarbonate Merits:
- Water soluble
- Acts instantly
- Potent neutralizer
- Raises pH above 7
Sodium Bicarbonate Demerits:
- Absorbed systemically
- Acid rebounds occur
- Increases sodium load
GI system anatomy and physiology questions
Gastrointestinal Short Essays
Question 1. Classify drugs used in peptic ulcer
Answer:
Peptic ulcer occurs in that part of the gastrointestinal tract which is exposed to gastric acid and pepsin. Produces carbon dioxide in the stomach
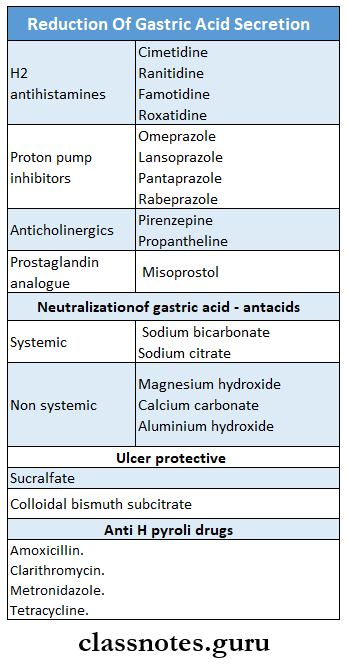
Classify drugs used in peptic ulcer Classification:
- Drugs used in the treatment of peptic ulcer are:
1. Reduction of gastric acid secretion
- H2 Antihistamines
- Cimetidine, Ranitidine, Famotidine, Roxatidine, Loxatidine
- Proton pump inhibitors
- Omeprazole, Lansoprazole, Pantoprazole, Rabepra- zole
- Anticholinergic
- Pirenzepine, Propantheline
- Prostaglandin analogs
- Misoprostol
2. Neutralization of gastric acid- antacids
- Systemic antacids
- Sodium bicarbonate
- Sodium citrate
- Nonsystemic antacids
- Magnesium hydroxide
- Magnesium trisilicate
- Aluminum hydroxide gel
- Magaldrate
3. Ulcer protective
- Sucralfate, colloidal bismuth substrate
4. Anti-H pylori drugs
- Amoxicillin, metronidazole, Clarithromycin
Question 2. Antihistaminic drugs used in peptic ulcer.
(or)
H2 blockers
Answer:
- Antihistaminic drugs or H2 blockers are:
- Cimetidine, Ranitidine, Famotidine, Roxatidine, Loxatidine
- They are highly effective drugs
H2 blockers Actions:
1. H2 blockade-Causes:
- Blockade of histamine-induced gastric secretion
- Cardiac stimulation
- Uterine relaxation
- Bronchial relaxation
- Fall in BP
2. Gastric secretion
- Inhibition of gastric secretion
- Prevention of gastric ulceration occurring due to stress and drugs
Gastrointestinal pharmacology Q&A
H2 blockers Uses:
- Duodenal ulcer- provides rapid and marked pain relief
- Gastric ulcer- Heal NSAID-associated ulcers
- Stress ulcers- Occurring in situations like severe burns, trauma, prolonged surgery, etc.
- Zollinger-Elison syndrome
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease
- Prophylaxis of aspiration pneumonia
H2 blockers Adverse Effects:
- Headache, dizziness, bowel upset, dry mouth, rashes
- CNS effects- confusion, restlessness, hallucinations
- Antiandrogenic effect of cimetidine
Question 3. Ranitidine
Answer:
- Ranitidine is an H2 receptor blocker
Ranitidine Uses:
- Duodenal ulcer- provides rapid and marked pain relief
- Gastric ulcer- Heal NSAID-associated ulcers
- Stress ulcers- Occurring in situations like severe burns, trauma, prolonged surgery, etc.
- Zollinger-Elison syndrome
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease
- Prophylaxis of aspiration pneumonia
Ranitidine Advantages:
- More potent
- Longer-acting
- Has no antiandrogenic effects
- No CNS effects as it does not cross BBB
- Does not inhibit microsomal enzymes
- Has mild side effects
Question 4. Antacids
Answer:
Antacids:
- Antacids are basic substances that neutralize gastric acid and raise the pH of gastric contents.
Antacids Classification:
1. Systemic antacids
- Sodium bicarbonate
- Sodium citrate
2. Nonsystemic antacids
- Magnesium hydroxide
- Magnesium trisilicate
- Aluminum hydroxide gel
- Magaldrate
Antacids Uses:
- For intercurrent pain relief and acidity
- Nonulcer dyspepsia
- Minor episodes of heartburn
- Reflux esophagitis
Nursing questions on GI system
Antacids Disadvantages:
- Needed in large and frequent dose
- Inconvenient
- Can cause acid rebound and bowel upset
- Poor patient acceptability
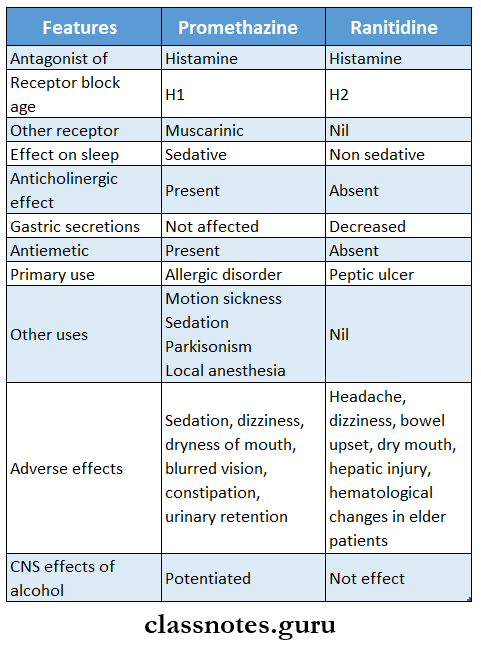
Question 5. Compare promethazine and Ranitidine
Answer:
Question 6. Emetics
Answer:
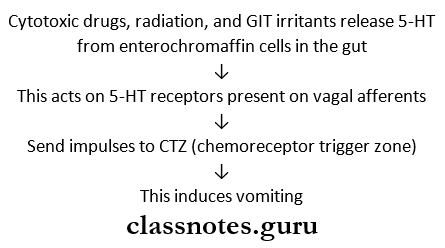
Emetics are drugs that produce vomiting
Emetics Mechanism:
Emetics Uses:
- To induce vomiting when noxious substances are ingested
Emetics Drugs Used:
- Mustard powder-1 teaspoon with water
- Hypertonic salt solution
- Apomorphine- SC/ IM
- Ipecacuanha-15-20 ml
Emetics Contraindications:
- Corrosive poisoning
- CNS stimulant drug poisoning
- Kerosene or petroleum poisoning
- In unconscious patients
Gastrointestinal diseases MCQs with answers
Question 7. Metoclopramide
Answer:
- Metoclopramide is widely used as antiemetic
Metoclopramide Actions:
- Increases gastric peristalsis
- Relaxes the pylorus and the first part of the duodenum
- Speeds up gastric emptying
Metoclopramide Mechanism of Action:
- Blocks D2 dopamine receptors in the CTZ
- Enhances acetylcholine release from the cholinergic neurons in the gut
Metoclopramide Uses:
- Antiemetic- in postoperative, drug-induced, disease-associated vomiting
- Gastrokinetic- To accelerate gastric emptying
- Before induction of general anesthesia
- To assist the passage of the tube into the duodenum
- To relieve diabetes-associated gastric stasis
- Dyspepsia
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease- provides symptomatic relief
Metoclopramide Adverse Effects:
- Sedation
- Dizziness
- Diarrhea
- Muscle dystonia
- Long-term use causes:
- Parkinsonism
- Galactorrhoea
- Gynaecomastia
Question 8. Prokinetic Agents
Answer:
Drugs that promote gastrointestinal and speedy gastric emptying are called prokinetic agents.
They are as follows:
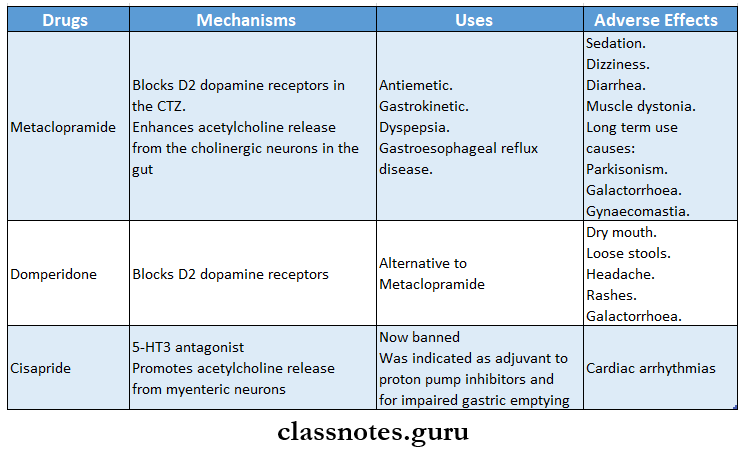
Question 9. Rationale of using domperiodone as antiemetics
(or)
Domperidone is preferred over Metaclopra- mide in vomiting
Answer:
- Domperidone is D2 antagonist
- Its action is not blocked by atropine
- It crosses the blood-brain barrier poorly
- It does not have extrapyramidal side effects
- Side effects of Domperidone are much less than that with Metadopramide
- It includes only dry mouth, loose stools, headache, rashes, galactorrhoea
- Thus it is preferred over Metadopramide as an Antiemetic
Digestive system questions and answers
Question 10. Mention two antiemetics.
Answer:
Antiemetics:
- Metoclopramide
- Domperidone
Question 11. Drugs used as purgatives
Answer:
- Purgatives are drugs that promote defecation
- They are also called laxatives
Purgatives Classification:
1. Bulk-forming
- Dietary fiber- Bran, plantago seeds, is Paula, methylcellulose
2. Stool softener
- Docusates, liquid paraffin
3. Stimulant Purgatives
- Diphenylmethanes
- Phenolphthalein, bisacodyl
- Anthraquinones
- Senna, cascara sagrada
- 5-HT4 agonist
- Tegaserod
4. Osmotic Purgatives
- Magnesium salts- sulfate, hydroxide
- Sodium salts- sulfate, phosphate
- Sodium potassium tartrate
Purgatives Mechanisms:
Increases water content of feces by
1. Osmotic action

3. Secondary effects
- Increases propulsive activity
- Decreases time for absorption
Purgatives Uses:
- In functional constipation
- In bedridden patients
- To avoid straining at stools
- Preparation of bowel for surgery, colonoscopy, abdominal X-ray
- After certain antihelminthic
Question 12. ORS
Answer:
- Oral rehydration solution is used in patients with diarrhea to replenish the lost water
ORS Composition:
- NaCl -3.5 g
- KC1 -1.5 g
- Trisodium citrate -2.9 g
- Glucose -20 g
- Water-1 liter
ORS Uses:
- To replace fluids and salts lost from the body during diarrhea
- To restore and maintain hydration
- Maintain electrolyte and pH balance
- Maintain hydration in patients postsurgically after burns, trauma, and in heat stroke
Question 13. The rationale for using loperamide in diarrhea
Answer:
- Loperamide is an opiate analog
- It is the potent constipating agent
- It has a poor water solubility
- Entry of it into the brain is negligible
- So it has no CNS effects occur
- It also inhibits GIT secretions
- Abdominal cramps and rashes are common adverse effects.
- Thus it is preferred for diarrhea
Question 14. PPIs (proton pump inhibitors)
Answer:
- Proton pump inhibitors are the most efficient inhibitors of the gastric acid secretion
- They are given as enteric-coated granules to avoid degeneration by the acid in the stomach
- They are:
- Omeprazole
- Lansoprazole
- Pantoprazole
- Rabeprazole
- Dexrabeprazole
- Esomeprazole
PPIs (proton pump inhibitors) Mechanism of Action:
- Proton pump inhibitors get accumulated in the parietal cells

PPIs (proton pump inhibitors) Uses:
1. Peptic ulcers
- Given for 4-8 weeks
- Ulcers heal fast
- Relief of pain is rapid and excellent
2. Gastroesophageal reflux disease
- Produces rapid symptomatic relief
- It is more effective than H2 blockers
3. Use in H. pylori treatment regimen
4. Zollinger- Ellison syndrome
PPIs (proton pump inhibitors) Adverse Effects:
- Adverse effects are minimal
- They occur rarely
- It includes:
- Nausea
- Loose stools
- Headache
- Abdominal pain
- Muscle and joint pain
- Dizziness
- Rashes
- Leucopenia
- Hepatic dysfunction
GI nursing management questions and answers
Gastrointestinal Short Question and Answers
Question 1. H2 antagonist
Answer:
- Antihistaminic drugs or H2 blockers are:
- Cimetidine, Ranitidine, Famotidine, Roxatidine, Loxatidine
- They are highly effective drugs
Question 2. Cimetidine
Answer:
- Cimetidine is an H2 blocker
- It was the first H2 blocker to be introduced
Cimetidine Uses:
- Duodenal ulcer- provides rapid and marked pain relief
- Gastric ulcer- Heal NSAID-associated ulcers
- Stress ulcers- Occurring in situations like severe burns, trauma, prolonged surgery, etc.
- Zollinger-Elison syndrome
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease
- Prophylaxis of aspiration pneumonia
Question 3. Antacids
Answer:
Antacids are basic substances that neutralize gastric acid and raise the pH of gastric contents.
Antacids Classification:
1. Systemic antacids
- Sodium bicarbonate
- Sodium citrate
2. Nonsystemic antacids
- Magnesium hydroxide
- Magnesium trisilicate
- Aluminum hydroxide gel
- Magaldrate
Question 4. Sucralfate
Answer:
Sucralfate is an ulcer protective agent
Sucralfate Mechanism:
- In an acidic medium, Sucralfate polymerizes to form a sticky, viscid gel
- This adheres firmly to the base of the ulcer
- Act as a physical barrier preventing acid, pepsin, and bile from coming in contact with ulcer base
- Stimulates prostaglandin secretion and promotes healing
Sucralfate Uses:
- Duodenal ulcer
- Gastric ulcer
Sucralfate Adverse Effects:
- Constipation
- Dry mouth
Common GI diseases short answer questions
Question 5. Carbenoxolone sodium
Answer:
- Carbenoxolone sodium is a steroid-like compound
- It is obtained from glycyrrhizic acid
Carbenoxolone sodium Mechanism of Action:
- It alters the composition of mucous
- Makes it more viscid
- Gets adheres to the gastric mucosa
- Protects the ulcer base
- Inhibits pepsin activity
- Prolong action of prostaglandin
Carbenoxolone sodium Adverse Effects:
- It causes salt and water retention so it is not preferred
Question 6. Omeprazole is used in peptic ulcer
Answer:
- Omeprazole is a proton pump inhibitor
- It is used in the treatment of peptic ulcer due to the following mechanism

Question 7. Ranitidine
Answer:
- Ranitidine is an H2 receptor blocker
Ranitidine Uses:
- Duodenal ulcer- provides rapid and marked pain relief
- Gastric ulcer- Heal NSAID-associated ulcers
- Stress ulcers- Occurring in situations like severe burns, trauma, prolonged surgery, etc.
- Zollinger-Elison syndrome
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease
- Prophylaxis of aspiration pneumonia
Question 8. Magnesium sulfate
Answer:
- Magnesium sulfate is a uterine relaxant
Magnesium sulfate Uses:
- To control convulsions
- To reduce BP in toxemia of pregnancy
- To suppress uterine contractions
Magnesium sulfate Adverse Effects:
- Cardiac arrhythmias
- Muscular paralysis
- CNS depression
- Respiratory depression
GI system assessment nursing questions
Question 9. Prokinetic drugs
Answer:
- Drugs that promote gastrointestinal motility and speed gastric emptying are called prokinetic agents
- Drugs that are used as prokinetic drugs are
- Metoclopramide
- Domperidone
- Cisapride
- Mosapride
- Tegaserod
Question 10. Aluminum hydroxide
Answer:
- Aluminum hydroxide is a weak and slow-acting antacid
- Food interferes with its action
- It is an astringent, so it forms a protective coating over the ulcers
- The aluminum ions relax smooth muscle
- It delays gastric emptying
- It binds to phosphate and prevents its absorption
- It causes constipation
Question 11. Metoclopramide
Answer:
- Metoclopramide is widely used as antiemetic
Metoclopramide Uses:
- Antiemetic- in postoperative, drug-induced, disease-associated vomiting
- Gastrokinetic- To accelerate gastric emptying
- Before induction of general anesthesia
- To assist the passage of the tube into the duodenum
- To relieve diabetes-associated gastric stasis
- Dyspepsia
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease- provides symptomatic relief
Metoclopramide Adverse Effects:
- Sedation
- Dizziness
- Diarrhea
- Muscle dystonia
- Long-term use causes:
- Parkinsonism
- Galactorrhoea
- Gynaecomastia
Question 12. Cimetidine and Ranitidine
Answer:
- Cimetidine and ranitidine are H2 blockers
Cimetidine and Ranitidine Uses:
- Duodenal ulcer- provides rapid and marked pain relief
- Gastric ulcer- Heal NSAID-associated ulcers
- Stress ulcers- Occurring in situations like severe burns, trauma, prolonged surgery, etc.
- Zollinger-Elison syndrome
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease
- Prophylaxis of aspiration pneumonia
Cimetidine and Ranitidine Adverse Effects
- Headache, dizziness, bowel upset, dry mouth, rashes
- CNS effects- confusion, restlessness, hallucinations
- Antiandrogenic effect of cimetidine
Question 13. Ranitidine preferred over Cimetidine
Answer:
- Ranitidine is preferred over cimetidine because it is:
- More potent
- Longer-acting
- Has no antiandrogenic effects
- No CNS effects as it does not cross BBB
- Does not inhibit microsomal enzymes
- Has mild side effects
Question 14. Classify drugs used in peptic ulcers
Answer:
- Drugs used in the treatment of peptic ulcer are:
1. Reduction of gastric acid secretion
1. H2 Antihistamines
- Cimetidine, Ranitidine, Famotidine, Roxatidine, Loxatidine
2. Proton pump inhibitors
- Omeprazole, Lansoprazole, Pantoprazole, Rabepra- zole
3. Anticholinergic
- Pirenzepine, Propantheline
4. Prostaglandin analogs
- Misoprostol
2. Neutralization of gastric acid- antacids
1. Systemic antacids
- Sodium bicarbonate
- Sodium citrate
2. Non-systemic antacids
- Magnesium hydroxide
- Magnesium trisilicate
- Aluminum hydroxide gel
- Magaldrate
3. Ulcer protection.
- Sucralfate, colloidal bismuth substrate
4. Anti-H pylori drugs
- Amoxicillin, metronidazole, Clarithromycin
Peptic ulcer disease questions and answers
Question 15. The rationale of combining aluminum hydroxide gel and magnesium trisilicate as antacids
Answer:
- Aluminum hydroxide gel is slow-acting and delays gastric emptying
- Magnesium trisilicate is fast acting and hastens gastric emptying.
- Combining both leads to:
- Prolongs the action of the drug
- Makes it intermediate-acting
- Maximizes the wanted effects
- Minimizes the adverse effects
- Neutralizes luxating effect of magnesium trisilicate
- Neutralizes constipating effect of aluminum hydroxide
Question 16. Proton pump inhibitors
Answer:
- Protons pump Inhibitors are the most efficient. Inhibitors of the gastric add secretions
- They act by blocking the final step in gastric acid secretions
- They are inactive at neutral pH and only get activated at a pH less than 5
- They are
- Omeprazole
- Lansoprazole
- Pantoprazole
- Rabeprazole
Proton pump inhibitors Uses:
- Peptic ulcer
- Severe Gastroesophageal reflux disease
- The component in the H.pylori treatment regimen
- Zollinger Ellison syndrome
Question 17. Aspirin is contraindicated in peptic ulcers
Answer:
- Aspirin is contraindicated in peptic ulcer because:
- It irritates gastric mucosa
- It causes gastric distress, nausea, vomiting
- It stimulates CTZ
- In the acidic pH of the stomach, it remains in an unionized form
- Drug particles get attached to the gastric mucosa
- They promote back diffusion of acid in the stomach
- It inhibits prostaglandin synthesis
- Inhibits gastric acid secretions
- Increases production of the mucosa
- This leads to the occurrence of ulcers
- This leads to reduced platelet aggregation
- Promotes bleeding in ulcers
Gastrointestinal tract functions questions
Question 18. Name two drugs used to suppress vomiting
Answer:
- Drugs used to suppress vomiting are called antiemetics
Suppress Vomiting Classification:
- Anticholinergics- Hyoscine, Dicyclomine
- HI antihistaminics- Promethazine, Diphenhydramine, Dimenhydrinate.
- Neuroleptics- Chlorpromazine, prochlorperazine
- Prokinetic drugs- Metoclopramide, Domperidone, Cisapride
- 5-HT3 antagonists- Ondansetron
- Adjuvant antiemetics- Dexamethasone, benzodiazepines
Question 19. The rationale for using Metoclopramide in vomiting
Answer:
- Metoclopramide is used in vomiting because it
- Increases gastric peristalsis
- Relaxes the pylorus and the first part of the duodenum
- Speeds up gastric emptying
- Blocks D2 dopamine receptors in the CTZ
- Enhances acetylcholine release from the cholinergic neurons in the gut
Question 20. Promethazine
Answer:
- Promethazine is a highly sedative H1 antagonist
Promethazine Uses:
- Allergic disorders
- Pruritis
- Common cold
- Preanasethetic medication
- Parkinsonism
Question 21. Bulk purgatives
Answer:
- Bulk purgatives include
- Bran
- Plantago seeds
- Agar
- Methylcellulose
- Ispaghula husk
- These are indigestible vegetable fiber and hydrophilic colloids
- It increases volume and lowers the viscosity of intestinal contents
- Used for prevention and treatment of functional constipation
- It requires daily administration for at least 3-4 days
- It forms a large, soft, and solid stool
- A large amount of water must be taken with it
Question 22. Name two osmotic purgatives
(or)
Osmotic purgatives
Answer:
- Osmotic purgatives are solutes that are not absorbed in the intestine
- They retain water osmotically, increase the bulk of intestinal contents, distend bowel, and increase peristalsis to evacuate a fluid stool
- They include
1. Nonabsorbable salts- saline Purgatives
- Magnesium hydroxide
- Magnesium sulfate
- Sodium potassium tartrate
- Sodium sulfate
- Phosphate
2. Nonabsorbable sugars- lactulose
3. Polyethyleneglycol
GI infections pharmacology questions
Question 23. Mention two drugs used in noninfective diarrhea
Answer:
- Drugs used in noninfective diarrhea are:
- Codeine
- Diphenoxylate
- Loperamide
Question 24. Loperamide
Answer:
- Loperamide is an opiate analog
- It is a potent constipating agent
- It has a poor water solubility
- Entry of it into the brain is negligible
- So no CNS effects occur
- It also inhibits GIT secretions
- Abdominal cramps and rashes are common adverse effects
- It is preferred for diarrhea
Question 25. Liquid paraffin
Answer:
Liquid paraffin Advantages
- Liquid paraffin is a viscous inert mineral oil
- It is a mixture of petroleum hydrocarbons
- It lubricates and softens feces
- It is taken for 2-3 days
Liquid paraffin Disadvantages:
- Unpleasant to swallow
- Interferes with the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins
- Aspiration may cause lipoid pneumonia
- May leak out of the anus causing discomfort
- If absorbed in the intestines causes foreign body granulomas
Question 26. Saline purgatives
Answer:
- Saline Purgatives are nonabsorbable salts
- It includes
- Magnesium hydroxide
- Magnesium surface
- Sodium potassium tartrate
- Sodium sulfate
- Phosphate
- They produce 1-2 fluid evacuations within 1-3 hours with mild cramping
- Causes nearly complete emptying of the bowel
Saline purgatives Uses:
- For the preparation of the bowel before surgery and colonoscopy
- In food/drug poisoning
- In the treatment of tapeworm infestations
Question 27. Anthraquinone preparations
Answer:
- Senna and Cascara sagrada are popular anthraquinone preparations
- They contain anthraquinone glycosides
- They are usually administered at bedtime to produce their effect in the morning
- They take 6-8 hours to act
- They are not absorbed in the small intestine
- They pass to the colon where bacteria liberate the active natural form which is later absorbed into the circulation
Anthraquinone preparations Adverse Effects:
- Skin rashes
- Black pigmentation of colonic mucosa
- Discoloration of urine
- Cramps and excessive purging
Anthraquinone preparations Contraindications:
- It is contraindicated in lactating mothers
Question 28. Hazards of use of purgatives
Answer:
- Regular use of purgatives may cause
- Gastrointestinal disturbances
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- Loss of electrolytes
- Loss of salts like calcium in stools
- Malabsorption
- Excessive dehydration may lead to death
Question 29. List two purgatives giving an indication for each.
Answer:
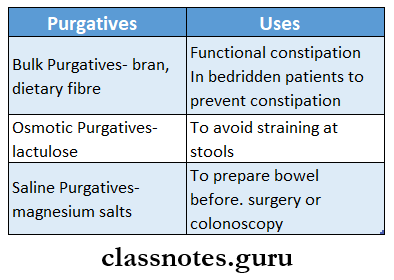
Short and long questions on gastrointestinal disorders
Question 30. Mechanism of action and two uses of Domperidone.
Answer:
Domperidone Mechanism of Action:
- It blocks the D2 receptor in CTZ
Domperidone Uses:
- As an antiemetic – alternative to metoclopramide
- As pre-anesthetic medication – to reduce postoperative vomiting
