Drugs Acting On Kidney Important Notes
1. Classification of diuretics
- High ceiling diuretics
- Furosemide
- Bumetanide
- Torsemide
- Moderate efficacy diuretics
- Thiazides – chlorothiazides, hydrochlorothiazides
- Thiazide related agents – chlorthalidone,, clopamide
- Low efficacy diuretics
- Potassium sparing diuretics – triamterene, amiloride, spironolactone
- Carbonic anhydrase inhibitor – acetazolamide .
- Osmotic diuretics – Mannitol, urea
- Methylxanthines – theophylline
- Newer agents
- Vasopressin antagonists
- Conivaptan
Drugs acting on kidney questions and answers
Read And Learn More: Pharmacology Question and Answers
Diuretics Drugs
2. Complications of high ceiling diuretics and thiazides
- Hypokalaemia
- Dilutional hyponatremia
- GIT and CNS disturbances
- Hearing loss
- Magnesium depletion
- Hyperuricaemia
- Hyperglycaemia
- Hyperlipidaemia
- Acute saline depletion
- Fall in BP
3. Drugs contraindicated in renal failure are
- Cephalothin
- Cephaloridine
- Nalidixic acid
- Nitrofurantoin
- Talampicillin
- Tetracyclines
Diuretics Drugs
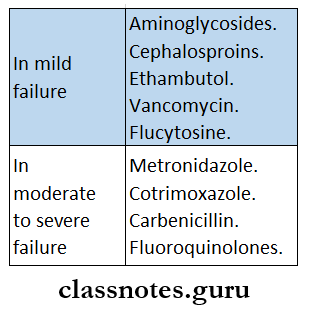
4. Drugs that require dose reduction in renal failure are:
Drugs Acting On Kidney Short Essays
Question 1. Classify diuretics. Write the mechanism of action of thiazides
Answer:
Diuretics:
- Drugs that increase urine and solute excretion causing loss of sodium and water from the body are called diuretics.
Diuretics Classification:
1. High efficacy or loop diuretics
- Furosemide, Bumetanide, Torasemide
2. Medium efficacy diuretics
- Benzothiadiazine or thiazides
- Hydrochlorothiazide, Benzthiazide
- Thiazides like drugs
- Chlorthalidone, Metolazone
Diuretics Drugs
3. Low efficacy or weak diuretics
- Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
- Acetazolamide
- Potassium sparing diuretic
- Aldosterone antagonist- spironolactone
- Inhibitors of renal epithelial sodium channel- Triamterene, amiloride
- Osmotic diuretics
- Mannitol, isosorbide, Glycerol
Mechanism of Action of Thiazides:

Renal pharmacology Q&A
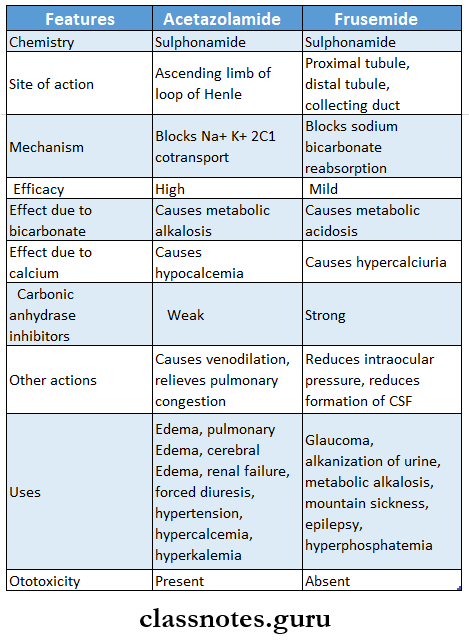
Question 2. Compare acetazolamide and frusemide.
Answer:
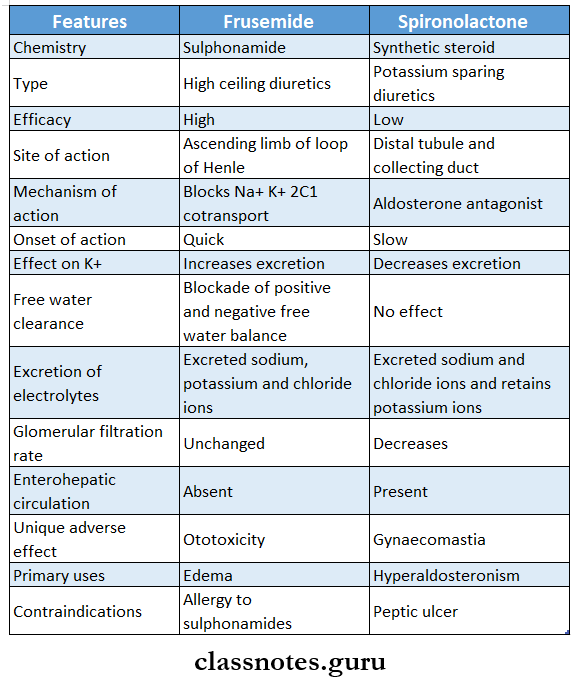
Question 3. Compare frusemide and spironolactone
Answer:
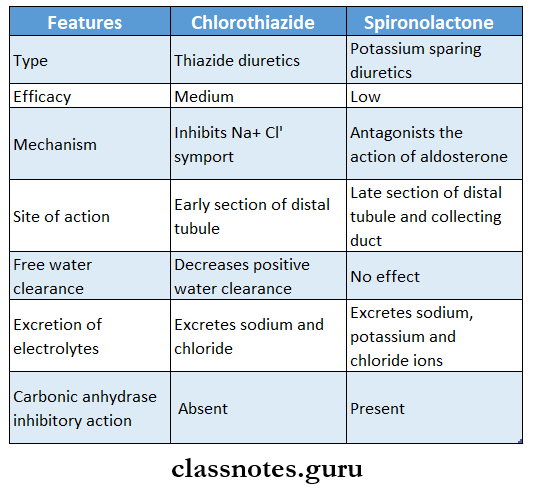
Question 4. Compare chlorothiazide and spironolactone
Answer:
Diuretics Drugs
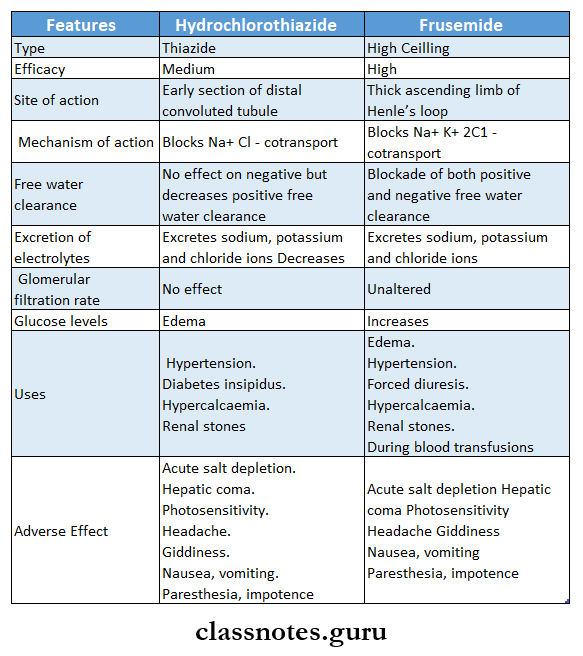
Question 5. Compare Hydrochlorothiazide and frusemide
Answer:
Question 6. Chlorothiazide
Answer:
- Chlorothiazide is a medium efficacy thiazide diuretics
Chlorothiazide Uses:
- Hypertension
- Congestive cardiac failure
- Hepatic or renal edema –
- Hypercalciuria with renal stones
- Diabetes insipidus
Chlorothiazide Adverse Effects:
- Hypokalaemia
- Carbohydrate intolerance
- Fatigue, loss of energy
- Impotence
- Hyperlipidaemia, hyperuricemia
- Decreased libido
Diuretics pharmacology questions and answers
Question 7. Mention two therapeutic uses and two adverse effects of frusemide.
Answer:
Frusemide:
- It is high efficacy diuretics
Frusemide Uses:
- Edema
- Hypertension
- Forced diuresis
- Hypercalcaemia
- Renal stones
- During blood transfusions
Frusemide Adverse Effects:
- Acute salt depletion
- Hepatic coma
- Photosensitivity
- Headache
- Giddiness
- Nausea, vomiting
- Paresthesia, impotence
Question 8. Complications of diuretics.
Answer:
1. Hypokalaemia
- Occurs with high ceiling diuretics and thiazides
- Characterized by weakness, fatigue, muscle cramps, cardiac arrhythmias
- Treatment:
- High dietary potassium intake
- Supplements of KC1
- Concurrent use of potassium-sparing diuretics
2. Acute saline depletion
- Causes dehydration and a fall in blood pressure
3. Hyponatremia – more with high ceiling diuretics
4. GIT disturbances – nausea, vomiting, diarrhea
5. CNS disturbances – headache, giddiness, weakness, paraesthesia
6. Hearing loss – with high-ceiling diuretics
7. Hypersensitivity – skin rashes, feverhyperuricaemia – with long-term use of thiazides
8. Hyperglycaemia, hyperlipidemia – when diuretics are used as antihypertensives
9. Magnesium depletion – due to prolonged use
10. Hyperkalaemia – with potassium-sparing diuretics
Drugs affecting kidney function short notes
Drugs Acting On Kidney Short Question And Answers
Question 1. Potassium-sparing diuretics
Answer:
- Potassium-sparing diuretics are:
- Spironolactone
- Triamterene
- Amiloride
Potassium-sparing diuretics Mechanism:
- Act as aldosterone antagonists
- Directly inhibit ion channels
Potassium-sparing diuretics Site of Action:
- Act as aldosterone antagonists
- Directly inhibits ion channels
Potassium-sparing diuretics Uses:
- Used along with thiazides and loop diuretics to prevent potassium loss
- Edema
- Hypertension
- Aldosteronism
BSc Nursing drugs on kidney questions
Question 4. Mannitol
Answer:
- Mannitol is an osmotic diuretics
- It helps to retain water in the proximal convoluted tubule and the descending limb of the Henle’s loop by osmosis
- This causes water diuresis and loss of sodium
- They are ineffective when given orally
- So it is given IV
Mannitol Uses:
- To maintain urine volume and prevent oliguria during hemolysis and shock.
- Used in the reduction of intracranial and intraocular pressure
Mannitol Adverse Effects:
- Dehydration
- ECF volume expansion
- Headache
- Hyperallergic reactions
Question 5. Spironolactone
Answer:
- Spironolactone is a potassium-sparing diuretic
- It is low efficacy diuretics
- It is an aldosterone antagonists
Spironolactone Uses:
- In the treatment of Hypercalcaemia and renal stones
- Along with other diuretics in the treatment of hypertension, to reduce hypokalaemia
- In the treatment of aldosteronism
Spironolactone Adverse Effects:
- Drowsiness
- Hyperkalemia in patients with renal insufficiency
- Gynaecomastia
- Skin rashes
Question 6. Loop diuretics
(or)
High ceiling diuretics
Answer:
- Loop diuretics are high efficacy diuretics
- They act by inhibiting sodium chloride reabsorption in the ascending limb of Henle’s loop
- They include
- Frusemide
- Bumetanide
- Piretanide
Loop diuretics Uses:
- Edema- cardiac, cerebral, hepatic, renal, pulmonary
- Hypertension
- Hypercalcaemia, Renal stones
- Hyperkalemia
- Barbiturate poisoning to induce forced diuresis
Pharmacology of renal drugs questions
Question 7. Osmotic diuretics
Answer:
- Osmotic diuretics include inert drugs like
- Mannitol
- Urea
- Glycerol
- It helps to retain water in the proximal convoluted tubule and the descending limb of the Henle’s loop by osmosis
- This causes water diuresis and loss of sodium
- They are ineffective when given orally
- So it is given IV
Osmotic diuretics Uses:
- To maintain urine volume and prevent oliguria during hemolysis and shock.
- Used in the reduction of intracranial and intraocular pressure
Osmotic diuretics Adverse Effects:
- Dehydration
- ECF volume expansion
- Headache
- Hyperallergic reactions
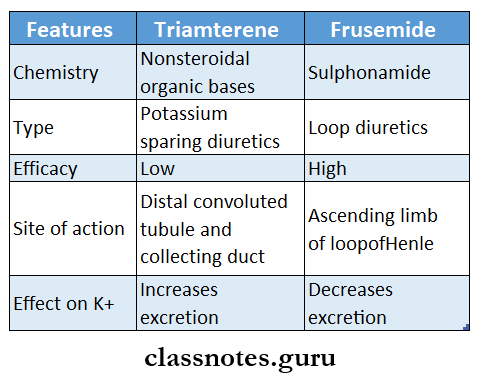
Question 8. Triamterene and frusemide
Answer:
Drugs acting on renal tubules pharmacology
Question 9. Rationale of combining thiazides with spironolactone
(or)
The rationale for combining spironolactone with frusemide
Answer:
- Frusemide and Thiazides cause excess excretion of potassium from the body
- The sodium present in the distal convoluted tubule may also be exchanged for potassium ions which may be excreted in the urine
- This may lead to hypokalaemia
- Spironolactone reduces potassium loss by inhibiting the action of aldosterone which is responsible for potassium secretion
- So spironolactone is combined with Frusemide or Thiazide
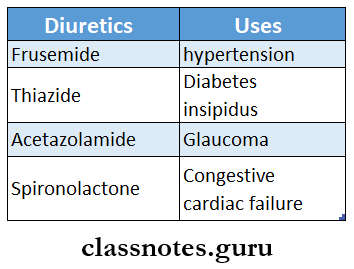
Question 10. Enlist three diuretic drugs and one different use for each.
Answer:
Nephrotoxic drugs questions and answers
Question 11. Name two loop diuretics. Mention two uses of them.
Answer:
Loop Diuretics:
- Frusemide
- Bumetanide
- Torasemide
Loop Diuretics Uses:
- Edema
- Acute Pulmonary Edema
- Hypertension
