Diseases Of The Gastrointestinal System Long Essays
Question 1. Describe the pathophysiology, clinical features, diagnosis & management of reflux oesophagitis.
Answer:
Reflux Oesophagitis
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
Definition:
- Reflux Oesophagitis is defined as the reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus resulting in inflammation of the esophagus caused by H+ ions, pepsin & bile salts.
Pathophysiology

Gastrointestinal system diseases long essay
Clinical Features:
- Heartburn
- Acid eructation.
- Painful swallowing.
- Transient dysphagia, n Strictures.
- Iron deficiency anaemia. b Hoarseness of voice.
- Acid erosion of incisors.
- Pneumonia.
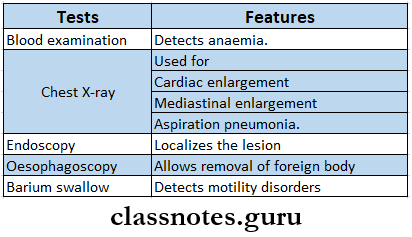
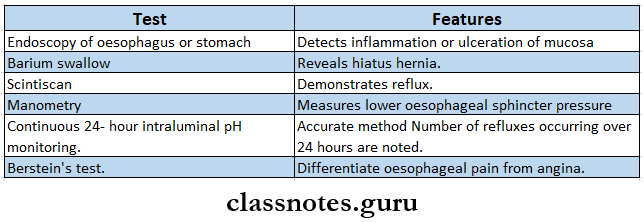
Diagnosis:
- General Measures
- Weight reduction
- Avoid alcohol & smoking.
- Avoid sleeping immediately after large meals.
- Avoid the use of analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Use of small volumes and frequent meals.
- Medical Measures:
- In mild cases.
- Liquid antacid – 10 – 15 ml 1 – 3 hours after meals.
- In moderate cases – H2 antagonists are used.
- Cimetidine – 400 mg.
- Ranitidine – 150 mg BD or QID with meals. & before bed for 6 weeks.
- In severe cases – proton pump inhibitors are used.
- Omeprazole – 20 – 40 mg/ day.
- Lansoprazole – 15 – 30 mg/ day.
- Pantaprazole – 40 mg/ day.
- Rabiprazole – 10 – 20 mg/day.
- Other
- Metoclopramide 10 mg TID increases the lower oesophageal sphincter.
- In mild cases.
- Surgical Treatment:
- Repair of the sphincter.
- Construction of additional valve mechanism.
Read And Learn More: General Medicine Question and Answers
Question 2. Describe etiology. Clinical features, diagnosis & management of peptic ulcer.
Answer:
Peptic Ulcer:
- It is defined as the presence of an ulcer in the lower esophagus, stomach, or duodenum, in the jejunum after surgery to the stomach.
- It is a breach in the mucosa.
Etiology:
- Hereditary.
- Helicobacter pylori infection.
- Smoking.
- Corticosteroids
- Acid-pepsin versus mucosal resistance.
- Alcohol consumption.
Pathogenesis:

Long essay on GI tract disorders
Peptic Ulcer Clinical Features:
- It is chronic condition
- Epigastric pain.
- Hunger pain – occurring in an empty stomach.
- Night pain – wakes the patient from sleep.
- Episodic pain.
- Excessive salivation.
- Heart bum.
- Loss of appetite.
- Nausea, vomiting anorexia.
- Haematemesis.
- Weight loss.
Peptic Ulcer Investigations:
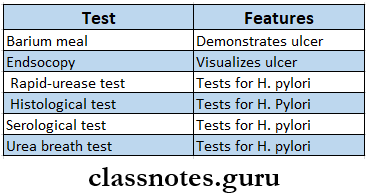
Peptic Ulcer Treatment:
- General Measures:
- Avoid smoking
- Avoid alcohol consumption
- Avoid NSAIDs
- Medical Treatment:
- Antacids
- 15 – 30 ml liquid, 1 – 3 hours after food and before bedtime for 4-6 weeks.
- H2 receptor antagonists.
- Cimetidine – 400 mg BD
- Ranitidine – 150 mg BD
- Proton pump inhibitor.
- Omeprazole – 20 mg daily for 4 – 8 weeks.
- Lansoprazole – 15 – 30 mg daily for 4-8 weeks.
- Pantaprazole – 40 mg daily for 4-8 weeks.
- Prostaglandin analogs.
- Misoprostol – 200 mg 4 times daily.
- Antacids
- Surgical Treatment:
- Truncal vagotomy + pyloroplasty.
- Partial gastrectomy.
- Elective surgery.
Question 3. Discuss the etiology, clinical features, and management of malabsorption syndrome.
Answer:
Malabsorption Syndrome:
- Malabsorption Syndrome refers to the defective absorption of one or more essential nutrients through the intestine.
Etiology:
- Pancreatic disorders.
- Chronic pancreatitis
- Cystic fibrosis
- Malignancy pancreas.
- Disorders causing deficiency of bile acids.
- Interruption of enterohepatic circulation.
- Abnormal bacterial proliferation in small intestine.
- Drugs like neomycin.
- Inadequate absorptive surface.
- Mucosal defects.
- Mucosal defects.
- Tropical sprue.
- Lymphoma.
- Amyloidosis.
- Biochemical or genetic abnormalities.
- Disaccharidase deficiency.
- Hypogammaglobulinaemia.
- Metabolic defects.
- Diabetes mellitus
- Addison’s disease
- Specific malabsorption.
- Lactose deficiency.
- Vitmai B12 malabsorption.
Malabsorption Syndrome Clinical Features:
- General Features:
- 3 health
- Loss of weight
- Lazziness, lassitude
- Fatigue, weakness.
- GIT symptoms
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal pain, distension.
- Stomatitis, glossitis, cheilosis.
- Genitourinary.
- Nocturia.
- Loss of libido.
- Hematopoietic.
- Anaemia.
- Skeletal
- Bone pain
- Tetany
- Muscle wasting
- Nervous system
- Night blindness
- Xerophthalmia.
- Peripheral neuropathy.
- Skin
- Purpura.
- Hyperkeratosis
- Edema of legs
Malabsorption Syndrome Management:
- Use of gluten-free diet.
- Use of a low-fat diet and cholestyramine.
- Replacement therapy for anemia, bone disease, and coagulation defects.
- Vitamins and minerals supplementation.
- Oral administration of folic acid & iron.
- Intravenous fluid administration for dehydration.
- Use of corticosteroids to suppress immunological responses.
Digestive system diseases long questions
Question 4. How will you investigate a case of dysphagia? Enumerate conditions causing dysphagia.
Answer:
Dysphagia:
- It is defined as difficulty in swallowing.
Dysphagia Causes:
- Mechanical narrowing of the esophagus.
- Intrinsic causes.
- Congenital atresia.
- Stomatitis, glossitis, tonsillitis, pharyngitis.
- Benign or malignant tumors.
- Oesophageal stricture or ulceration.
- Extrinsic causes.
- Retropharyngeal abscess.
- Enlarged thyroid gland.
- Aortic aneurysm.
- Intrinsic causes.
- Motor dysphagia.
- Lower motor neuron paralysis.
- Neuromuscular paralysis.
- Oesophageal muscle weakness.
- Paralysis of the oesophageal sphincter.
Dysphagia Investigations: