Disease Of The Hepatobiliary System
Hepatic Carcinoma
- Hepatic Carcinoma is the most common type of liver cancer
Hepatic Carcinoma Etiology:
- Hepatitis B and C infection.
- Alcoholism.
- Cirrhosis of the liver.
- Hemochromatosis.
- Wilsons disease.
- Oestrogen and androgen.
- Anabolic steroids.
Hepatic Carcinoma Clinical Features
- Yellow skin.
- Bloating from fluid in the abdomen.
- Easy bruising.
- Loss of appetite n Weight loss
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea, vomiting
- Fatigue.
- Poly ischemia, hypoglycemia, hypercalcemia.
Hepatic Carcinoma Diagnosis
- Serum alkaline phosphatase – high.
- Ultrasonography – shows carcinoma, lesion shows poorly defined margins.
- CT scan – detects small tumours.
- Angiography — shows tumor blushes.
- Liver aspiration – confirms tumour.
Hepatobiliary system diseases
Hepatic Carcinoma Management
- Liver transplantation.
- Surgical resection.
- Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE)
- Palliative therapy – use of cisplatin, and fluorouracil.
- Radiofrequency ablation.
Read And Learn More: General Medicine Question and Answers
Liver Abscess:
- Liver abscess is a pus-filled mass inside the liver.
Liver Abscess: Etiology
- Portal vein bacteremia from appendicitis, diverticulitis, and a perforated bowel.
- Systemic bacteremia via the hepatic artery.
- Ascending cholangitis.
- Penetrating trauma.
- Direct extension from focus of infection.
Liver Abscess Clinical Features
- Subacute in onset.
- Jaundice
- Abdominal pain.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Dark urine, clay-colored stools.
- Fever with chills.
- Loss of appetite.
- Weight loss.
- Weakness.
Liver Abscess Complications
- Pleural effusion.
- Perforation of abscess with peritonitis
- Subphrenic abscess.
- Empyema,
- Hepatic coma.
Liver and biliary diseases
Jaundice
Jaundice: Jaundice refers to yellow discoloration of skin, mucous membrane, sclera, and conjunctiva due to raised serum bilirubin.
Jaundice Classification
- Based on coloration of sclera.
- Medical jaundice – yellow coloration.
- Surgical jaundice – greenish-yellow coloration.
- Based on etiology of jaundice.
- Hemolytic.
- Hepatic
- Obstructive.
- Based on chemical nature of bilirubin.
- Unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia.
- Conjugated hyperbilirubinemia.
Jaundice Causes
- Jaundice with predominantly unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia.
- Hemolysis.
- Intracorpuscular or extracorpuscular defects.
- Drug-induced.
- Infections.
- Decreased uptake of bilirubin.
- Drugs
- Sepsis
- Congenital
- Decreased conjugation of bilirubin.
- Neonatal jaundice.
- Gilbert’s syndrome.
- Hemolysis.
- Jaundice with predominantly conjugated hyperbilirubinemia.
- Intrahepatic cholestasis.
- Congenital
- Drugs and alcohol.
- Hepatitis
- Primary biliary cirrhosis.
- Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
- Postoperative.
- Extrahepatic biliary obstruction.
- Bile duct stone
- Biliary stricture c Trauma
- Tumour
- Pancreatitis.
- Intrahepatic cholestasis.
Hepatobiliary disorders
Jaundice Clinical Features
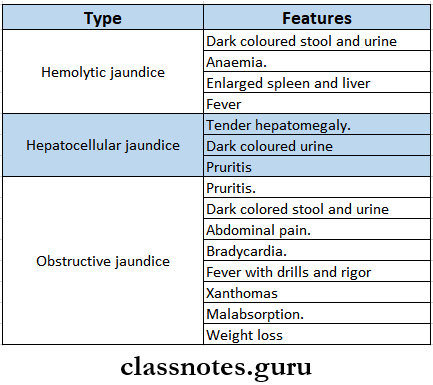
Jaundice Diagnosis
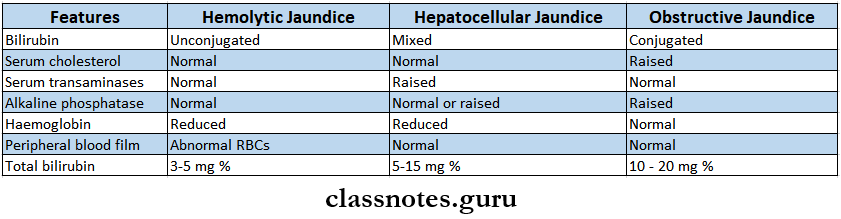
Jaundice Complications
- Sepsis
- Biliary cirrhosis
- Pancreatitis
- Coagulopathy
- Renal and liver disease
Jaundice Management
- Treat the causative agent.
- Discontinue the causative drug/toxin.
- Maintain adequate hydration and rest.
- Avoid alcohol.
- Use of analgesics to relieve pain, and antibiotics for infections.
- Blood transfusion.
Question 4. Describe the etiology, clinical features, complications diagnosis, and management of serum hepatitis B. Add a note on its prevention. (or) Enumerate the viruses causing acute hepatitis. Describe the clinical features and complications of viral hepatitis B. Add a note on the dental significance.
Answer:
Hepatitis: It is an acute parenchymal disease of the liver.
Viruses Causing Acute Hepatitis
- Specific viruses.
- Hepatitis A virus
- Hepatitis B virus
- Hepatitis C virus
- Hepatitis D virus
- Hepatitis E virus
- Other viruses.
- Cytomegalovirus
- Epstein barr virus.
- Herpes simplex virus.
Common liver diseases
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B: Etiology: Etiology is caused by the hepatitis B virus.
Hepatitis B Clinical Features:
- Prodromal symptoms – Anicteric phase.
- Occurs before the development of jaundice.
- Fever with chills, malaise
- Headache.
- Aches and pain.
- Nausea, vomiting, distaste for food.
- Disturbed smell.
- Dark-colored urine, clay-colored stools.
- It lasts for a few days to 2 weeks.
- Icteric phase.
- Jaundice occurs.
- Enlarged and tender liver
- Dark-colored urine, clay-colored stools
- Pruritus.
- Weight loss
- Recovery phase.
- It takes 2-8 weeks.
- Jaundice starts regressing.
- Full recovery occurs within 1-2 months.
Hepatitis B Complications
- Cirrhosis of the liver.
- Liver cancer
- Liver failure.
- Chronic renal diseases.
Hepatitis B Diagnosis
- Serum transaminases – Rises
- High serum alkaline phosphatase level
- Serum bilirubin – 5 – 20 mg %.
- Prothrombin time – normal.
- Urine urobilinogen – Increased
- Ultrasound of the liver – shows an enlarged liver.
Hepatitis B Treatment
- Bed rest.
- High-calorie diet.
- Intravenous fluid administration,
- Avoid hepatotoxic drugs
- Used of H2 blockers and antacids.
- Liver transplantation.
Hepatitis B Prevention
- Recombinant hepatitis B vaccine containing. HBs Ag is used for active immunization.
Gallbladder diseases
Hepatitis B Dental Significance
- A significantly higher incidence of HBV occurs among dental staff.
- Vectors of infection are blood, saliva, and nasopharyngeal secretion.
- Intraorally, the greatest concentration of hepatitis B infection is gingival sulcus,
- Also, periodontal disease, severity of bleeding, and bad oral hygiene are associated with the risk of HBV.
- All dental healthcare workers should receive vaccination against hepatitis B.
Question 5. Discuss the etiology, clinical features, complications, and treatment of cirrhosis of the liver.
Answer:
Cirrhosis Of Liver
- It is end result of hepatocellular injury characterized by a triad of pathological changes i.e.,
- Degeneration of hepatocytes.
- Hyperplasia of remaining hepatocytes.
- Fibrosis.
Cirrhosis Of Liver Causes
- Common causes.
- Alcohol.
- Hepatitis B, C, non-A, non-B, non-C, viruses.
- Other causes.
- Autoimmune hepatitis.
- Drug-induced.
- Biliary cirrhosis.
- Haemochromatosis
- Wilson’s disease
- Cardiac cirrhosis.
- Glycogen storage disease
- Idiopathic.
Cirrhosis Of Liver Clinical Features
- General
- Fever, jaundice, weakness, fatigue, weight loss.
- GIT symptoms:
- Ascites.
- Nausea, vomiting, anorexia.
- Abdominal distension.
- Splenomegaly.
- Haematemesis.
- Portal hypertension.
- Nodular and enlarged liver.
- Circulatory symptoms.
- Palmar erythema, spider angiomata, cyanosis, clubbing.
- Endocrine changes.
- Loss of axillary and pubic hair, loss of libido, gynaecomastia, amenorrhoea.
- Blood changes.
- Aneamia, pancytopenia, bruises, purpura, epitaxis.
Hepatobiliary disease symptoms
Cirrhosis Of Liver Complications
- Portal hypertension.
- Ascites
- Upper G1 bleeding
- Bacterial peritonitis.
- Hepatic encephalopathy n Hepatorenal syndrome.
- Hepatocellular carcinoma.
Cirrhosis Of Liver Treatment
- Removal of causative agent.
- General measures.
- Intake of high protein and high caloric diet.
- Avoid alcohol.
- Vitamin and minerals supplements.
- Low sodium diet.
- Use of diuretics.
- Water restriction.
- Treatment of complications.
- Liver transplantation.
Question 6. Define and describe the clinical features of ascites. Describe the pathogenesis and treatment of ascites.
Answer:
Ascites: An abnormal collection of fluid in the peritoneum is called ascites.
Ascites Pathogenesis:
1. Inflammation of peritoneum.
↓
Increased capillary permeability.
↓
Transudation of fluid into peritoneum
↓
Ascites
2. Venous obstruction
↓
Transudation of fluid into peritoneum
↓
Ascites
↓
Lymphatic obstruction → Ascites
Liver disease causes and treatment
Ascites Clinical Features
- Abdominal enlargement.
- Stretching sensation
- Low back pain
- Indigestion, heartburn
- Dyspnoea or tachypnoea.
- Abdominal or inguinal hermia.
- Hepatosplenomegaly.
Ascites Treatment
- Salt restriction
- Use of diuretics
- Therapeutic paraentesis.
- Cefotaxime – 1g 4 twice a day.
- Gentamicin – 60 – 80 mg 4 or IM 8 hourly.
