Defence Mechanism Of Gingiva Important Notes
1. Cells in Gingival Crevicular Fluid
- The predominant cell in GCF is PMNs- 92%
- Mononuclear cells contribute to 8%
2. Methods of collecting Gingival Crevicular Fluid (GCF)
- Placing filter paper into the sulcus – intra crevicular
- Placing paper at the entrance of sulcus- extra crevicular
- Placing preweighed twisted threads or micropipettes and crevicular washings
3. Methods of measuring the amount of Gingival Crevicular Fluid (GCF)
- The wetted area of the filter paper is stained with Ninhydrin and is measured parametrically under a microscope
- The electronic method using fluid collected on a blotter paper and employing perceptron
Read And Learn More: Periodontics Question and Answers
4. Glucose content of GCF is 3-4 times greater than in serum due to the metabolic activity of the adjacent tissues and the function of microbial flora. While the protein content of GCF is less than that of serum
- Functions of saliva
- Significance of gingival crevicular fluid
- Methods of Gingival crevicular fluid
- Composition of Gingival crevicular fluid (GCF)
- The defense mechanism of gingival
- Circadian periodicity
Defense Mechanism Of Gingival Short Essays:
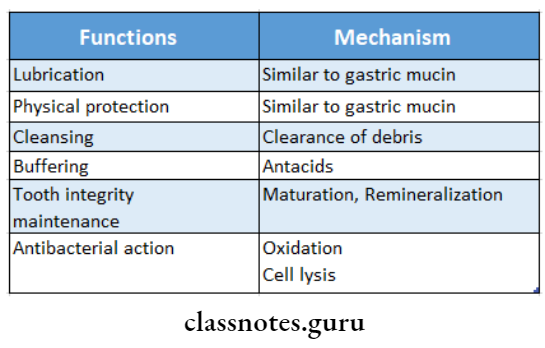
Question 1. Functions of Saliva.
Answer:
Question 2. Significance of Gingival Crevicular Fluid (GCF)
Answer:
1. Circadian periodicity:
- There is a gradual increase in Gingival Crevicular Fluid (GCF) amount from 6:00 AM to 10.00 PM and decreases afterward
- This is called Cicardian periodicity
2. Sex Hormones:
- Female sex hormones increase the flow
- Pregnancy, ovulation, and hormonal contraceptives increase gingival fluid
3. Smoking:
Causes an immediate transient increase in flow
4. Periodontal therapy:
Increase in gingival fluid during the healing period
Question 3. Methods of Collection of Gingival Crevicular Fluid (GCF)
Answer:
1. Absorbing paper strips:
Collection of Gingival Crevicular Fluid (GCF) Types:
- Intracrevicular – Insert paper in sulcus
- Extracurricular – Place at the entrance of the sulcus
Collection of Gingival Crevicular Fluid (GCF) Evaluation:
- Staining with alcohol
- Pre and post-weighing the papers
- Periotron electronic device
2. Micropipettes:
Analyze the amount of GCF collected in tubes by capillary action
3. Gingival washing:
A known amount of solution is introduced and removed into the Gingival sulcus
4. Other:
- Plastic strips/Platinum loops
- Inserted into sulcus and pressure is applied
Question 4. Composition of Gingival Crevicular Fluid (GCF)
Answer:
- Cells: Bacteria, Epithelial cells, Leukocytes (BEL)
- Electrolytes: Sodium, Potassium, Calcium
- Organic compounds: Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids
- Metabolic and Bacterial products: Lactic acid, Urea, Prostaglandins, Endotoxin
- Enzymes: Acid phosphatase, Alkaline phosphatase, Pyrophosphatase, lysozyme, Hyaluronate
Question 5. Defense Mechanism of Gingiva.
Answer:
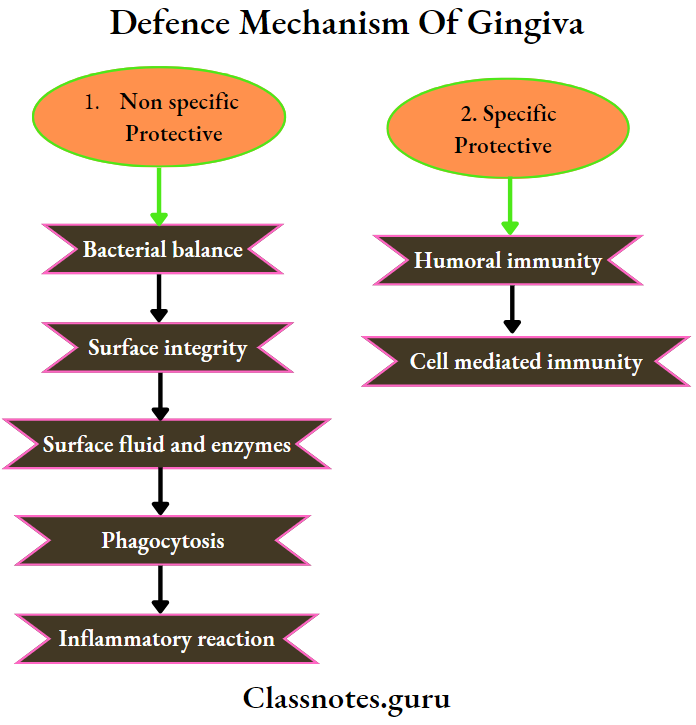
1. Non-specific Protective Mechanisms:
- Bacterial Balance:
- Balance exists between different species of microorganisms
- Surface Integrity:
- Maintained by the persistent renewal of the epithelium from its base and desquamation of surface layers
- This maintains the constant thickness of the epithelium
- Surface Fluid and Enzymes:
- Saliva contains antibacterial substances
- Gingival Crevicular Fluid (GCF) contains phagocytic leukocytes and enzymes
- Phagocytosis:
- Monocytes act in chronic infections
- PMNs act in acute infections
- Complements induce smooth muscle contraction, increase vascular permeability, and release histamine from mast cells.
- Inflammatory reaction:
- Stimulated by tissue injury and infections
- Results in hyperemia increased vascular permeability and formation of exudate
2. Specific Protective mechanism: My immune system
Protective mechanism Types:
- Humoral immunity
- Cell-mediated immunity
Defense Mechanism Of Gingiva Short Question And Answers
Question 1. Cicardian Periodicity.
Answer:
- Circadian Periodicity is a gradual increase in gingival fluid amount from 6:00 AM to 10.00 PM and decreases afterward
- This is called Cicardian periodicity
Question 2. Intracellular drug delivery.
Answer:
- Drugs that are excreted through the GCF may be used. This flow of neutrophils is important for protection from advantageously in periodontal therapy
- Such drugs are tetracycline and metronidazole
- These drugs are excreted in crevicular fluid when given systemically
- When these drugs are given locally, higher concentrations are achieved in the desired area leading to faster action
Question 3. Name the defense mechanism of the gingiva.
Answer:
Defence Mechanism Of Gingiva:
- Epithelial barrier
- GCF
- Saliva
- Orogranulocytes
Question 4. Granulocytes.
Answer:
- The viable neutrophils present in the saliva are termed orogranulocytes or salivary corpuscles
- In normal individuals, 30,000 neutrophils per minute enter the oral cavity via the gingival sulcus
- This flow of neutrophils is required for periodontal health
- Any defect in neutrophil function and chemotaxis is associated with early-onset periodontal disease in children’s caries
Defence Mechanism Of Gingiva Viva Voce
- The ratio of T: B lymphocytes is about 1:3 in GCF
- Predominant immunoglobulin in GCF is IgG
- Predominant immunoglobulin in saliva is IgA
