NCERT Solutions For Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Reproduction In Animals Long Answer Questions

Question 1. How can we say that fish exhibit external fertilisation?
Answer:
Female fish lay eggs in water while male fish release sperm in water. Sperm swim and reach the eggs of fish randomly due to water currents. When a sperm comes in contact with the viable egg, nuclei of both cells fuse to form a zygote. This process of fertilisation takes place in water outside the female body, hence, fertilisation is external in fishes.
Question 2. Hens and frogs are both oviparous, exhibiting different types of fertilisation, explain.
Answer:
Hens lay eggs after fertilisation, therefore their eggs are covered with a hard shell to protect the young ones. This shows that fertilisation in a hen is internal. The frogs on the hand lay both sperm and eggs in winter water before fertilisation. Thus, the fertilisation in frogs takes place in water, hence it is external.
NCERT Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Reproduction in Animals LAQs
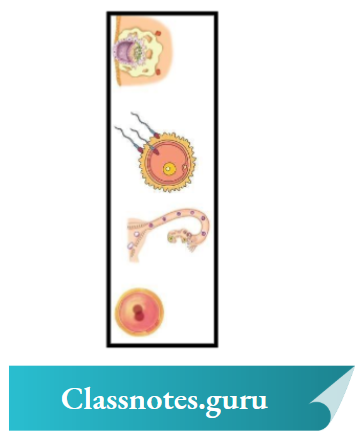
Question 3. The picture shows the basic parts of a salmon fish
Answer:
Part ‘Z’, which represents the tail of the sperm, helps it to swim in water and reach the egg.
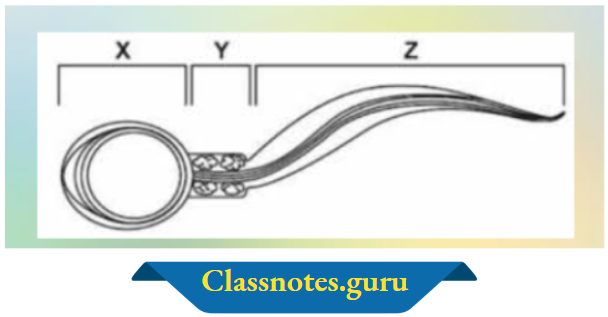
Which part of the sperm helps it to swim in water and reach the egg?
Answer:
Organ B is identified as the ovary
Question 4. Observe the diagram and answer the following questions
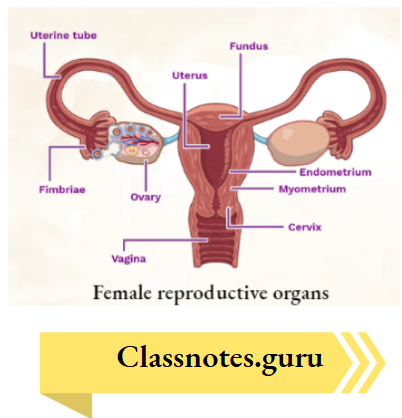
Answer: 1. Fallopian tube or oviduct.
1. Identify the organ B.
2. Whore does fertilisation occur In tho above diagram?
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
NCERT Solutions for Reproduction in Animals Chapter 6
Question 5. Observe the following figures.
Answer:
1. The figures showing stages during the development of the embryo are identified as
1. Identify the stages 1 to 4 in the figure during the development of the human baby.
Answer:
1. Embedding of the embryo in the uterus (implantation)
2. Arrange the stages in the correct sequence of development.
Answer: 2. Fertilisation (fusion of egg and sperm)

Reproduction in Animals Chapter 6 LAQs Class 8 NCERT
3. Explain the development that takes place in any one stage.
Answer:
3. Zygote formation and development of an embryo from the zygote.
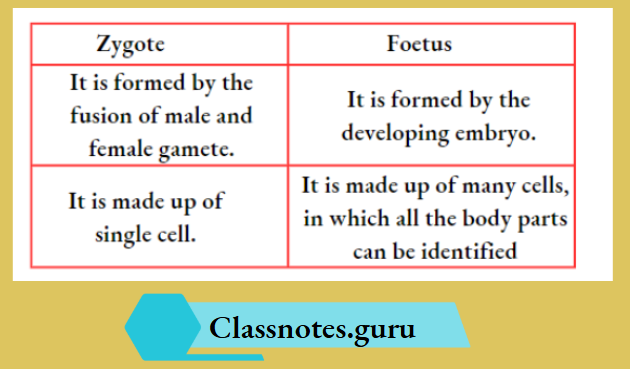
The embryo, after being implanted in the uterus, continues to develop and differentiate into body parts. This stage of the embryo is termed as foetus. After the foetus is completely developed, the mother gives birth to the baby.