Anticholinergic Drugs Important Notes
1. Anticholinergic drugs
- They inhibit the muscarinic actions of acetylcholine
- Examples
- Atropine
- Scopolamine
- Propantheline
- Methantheline
Read And Learn More: Pharmacology Question and Answers
2. Actions of atropine

3. Drugs causing mydriasis
- Anticholinergic drugs – atropine
- Adrenergic drugs – ephedrine, phenylephrine
4. Scopolamine/ Hyosine
- It is an anticholinergic drug
- Most effective drug for motion sickness
- Causes sedation
Anticholinergic drugs pharmacology
Anticholinergic Drugs Long Essays
Question 1. Classify anticholinergic drugs. Discuss pharmacological actions, uses & adverse effects of atropine. Mention symptoms of atropine poisoning and the line of treatment.
Answer:
Anticholinergic drugs:
- Anticholinergic drugs are agents which block the effects of acetylcholine on cholinergic receptors.
Anticholinergic drugs Classification:
1. Natural alkaloids – atropine, hyoscine.
2. Semisynthetic derivatives.
- Homatropine, atropine mononitrate hyoscine butyl bromide.
3. Synthetic compounds.
- Mydriatics – cyclopentolate.
- Antisecretory – antispasmodics.
- Quaternary compounds – propantheline.
- Tertiary amines – dicyclomine, pirenzepine.
- Vasicoselective – Oxybutynin, flavoxate.
- Anti parkinsonian – trihexyphenidyl, biperiden.
Atropine:
- It is the chief alkaloid of belladonna.
- Pharmacological actions.
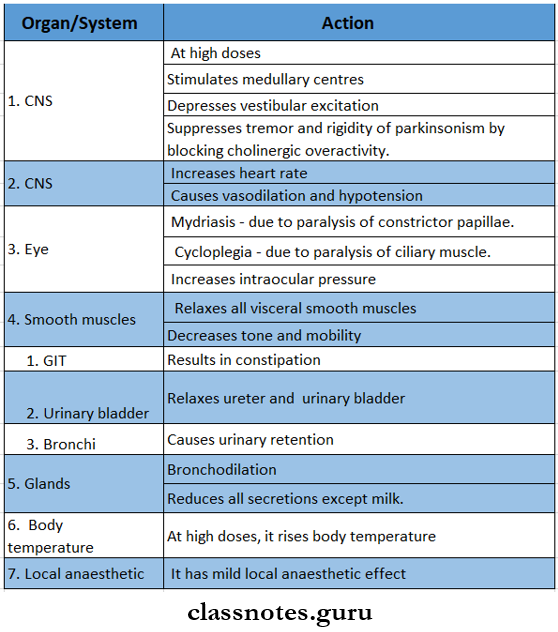
Atropine Uses:
- Preanaesthetic medication.
- Atropine is administered 30 minutes before surgery.
- This reduces salivary and respiratory secretions which prevent laryngospasm and bradycardia.
- As antispasmodic.
- In diarrhea and dysentery – reduces abdominal pain.
- Overcomes spasm of the sphincter of Oddi.
- In nocturnal enuresis – causes urinary retention.
- As mydriatic and cycloplegic.
- Used topically during refractory testing.
- Used in the treatment of iritis, keratitis, and corneal ulcer.
- Prevents adhesion between the iris and lens or the iris and cornea.
- In organophosphorus poisoning.
- In bronchial asthma, peptic ulcer
- Used in motion sickness.
- Used during labor to produce sedation and amnesia.
- Used in myocardial infarction to block vagal bradycardia.
- Pulmonary embolism – as it reduces reflex respiratory secretions.
- High doses lead to atropine poisoning.
Features of atropine poisoning:
- Palpitation.
- Excitement, psychotic behavior, ataxia, delirium, hallucination.
- Hypotension, weak and rapid pulse.
- Respiratory depression.
- Dilated pupil, photophobia, blurring of vision.
- Cardiovascular collapse, convulsions, coma.
Atropine Treatment:
- Ingested poison was removed by gastric lavage.
- Use cold sponging or ice bags to reduce body temperature.
- A drug used is physostigmine – 1 – 3 mg SC or IV, re¬peated 4-6 hourly.
- It antagonizes control and peripheral effects.
Anticholinergic drugs list
Question 2. Discuss atro¬pine. Mention some atropine substitutes and their uses in therapy.
Answer:
Atropine substitutes:
They aim at producing more selective action on certain functions.
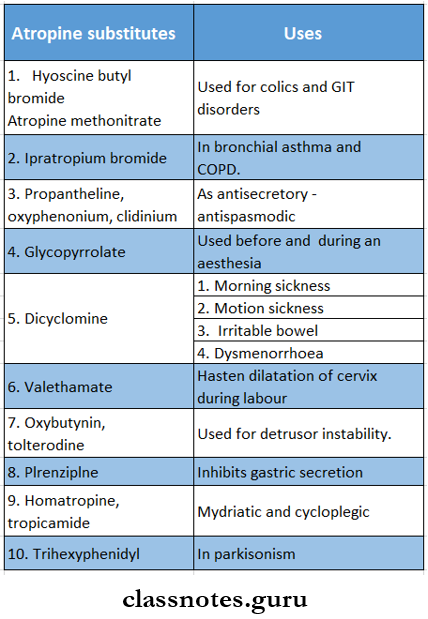
Anticholinergic Drugs Short Essays
Question 1. Compare atropine and cocaine.
Answer:
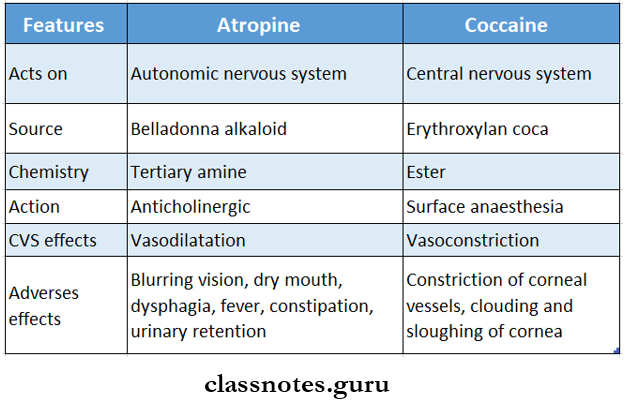
Question 2. Compare atropine and scopolamine.
Answer:
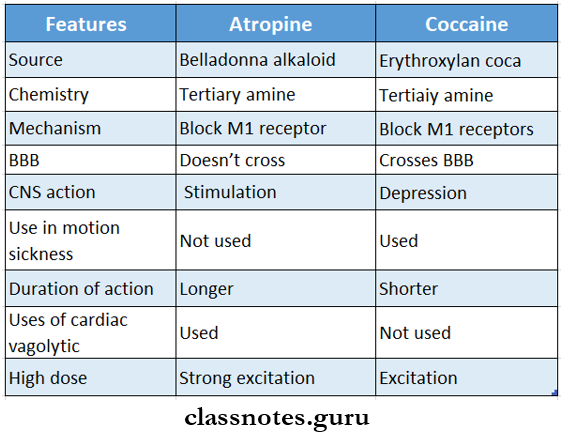
Anticholinergic drugs classification
Anticholinergic Drugs Short Answers
Question 1. Homatropine.
Answer:
Homatropine is an atropine substitute that is used on the eye.
- Homatropine causes mydriasis & cycloplegia that last for about 6 – 24 hours.
- They have shorter actions.
- Homatropine is used in atropine intolerance.
- Homatropine is formed to overcome the lack of sensitivity of belladonna alkaloids.
Question 2. The rationale of using atropine as pre-anesthetic medication.
Answer:
Atropine is administered 30 minutes before any surgery because.
- Atropine reduces salivary and respiratory secretion.
- This prevents laryngospasm.
- Atropine prevents bradycardia during surgery.
- Atropine acts as a bronchodilator.
- This reduces the risk of bronchial asthma related to anaphylactic shock.
Anticholinergic drugs mechanism of action
Question 3. Enlist six uses of anticholinergic drugs.
Answer:
- Preanaesthetic medication – to reduce secretions
- Antispasmodic – in diarrhea and colic
- Asmydriatric
- Parkinsonism – reduces tremors and rigidity
- Organophosphorous poisoning – atropine is used
- Motion sickness – hyoscine is given 30 minutes before the journey
- During labor – hyoscine is used to produce sedation and amnesia
Viva Voce:
- Atropine is used in organophosphorus poisoning
- Atropine is a CNS stimulant
- Scopolamine is CNS depressant
