Anti Parkisonian Drugs Important Notes
Anti Parkinsonian Drugs Parkinsonism
- It is an extrapyramidal motor disorder
- Characterized by
- Rigidity
- Tremor
- Hypokinesia
- Excessive salivation
- Dementia
- Mainly occurs due to the degeneration of nigrostriatal neurons which are dopaminergic
- Dopamine deficiency and cholinergic excess occur in it
- Drugs used for it are
- Levodopa – precursor of doapmine
- Carbidopa and benserazide – prevent decarboxylation of levodopa
Read And Learn More: Pharmacology Question and Answers
Anti Parkinsonian Drugs Long Essays
Question 1. Classify the drugs used in Parkinsonism. Discuss the pharmacology and adverse effects of L-dopa.
Answer:
Anti-parkinsonian drugs:
- These are drugs that have a therapeutic effect on Parkinsonism.
Anti-Parkisonian Drugs Classification:
1. Drugs affecting the brain’s dopaminergic system.
- Dopamine precursor – levodopa (L-dopa).
- Peripheral decarboxylase inhibitors – carbidopa, benserazide.
- Dopaminergic agonists – bromocriptine, ropinirole.
- MAO-B inhibitor – selegiline.
- COMT (Catechol-O-methyl transferase) inhibitor – entacapone, touch.
Anti-Parkisonian Drugs Levodopa (L-Dopa):
- Levodopa is the precursor of dopamine.
Levodopa Mechanism of action:
Levodopa crosses the blood-brain barrier.
↓
It is taken up by pre-synaptic terminals of dopaminergic
neurons.
↓
Dehydroxylation occurs.
↓
Causes the formation of dopamine.
Levodopa Actions:
1. CNS actions.
- Causes hypokinesia and rigidity resolution.
2. CVS actions:
- Causes tachycardia and postural hypotension.
3. CTZ [Chemoreceptor trigger zone]
- Stimulates CTZ to induce vomiting.
4. Endocrine.
- It acts on pituitary mamma tropes to inhibit prolactin release.
Levodopa Uses:
- Effective in idiopathic parkinsonism.
Levodopa Adverse effects:
- GIT symptoms – nausea, vomiting, anorexia.
- CVS affects – postural hypotension, tachycardia, palpitation, cardiac arrhythmia, and angina.
- Alteration in taste sensation.
- Abnormal movements – Dyskinesia, facial tics, grimacing, tongue thrusting.
- Behavioral effects – mild anxiety, nightmares, mania, hallucinations.
- Fluctuations in motor performance.
Anti-Parkinsonian drugs questions and answers
Anti-Parkinsonian Drugs Short Essays
Question 1. Explain why levodopa is given along with carbidopa.
Answer:
Decarboxylase inhibitor i.e., carbidopa prevents the conversion of levodopa to dopamine outside the brain by inhibiting the DOPA decarboxylase enzyme, peripherally.
- This combination can cross the blood-brain barrier and reaches its site of action in the brain.
- Other benefits obtained by this combination are:
- It reduces the dose of levodopa Upton approx 1/4th
- The plasma half-life of levodopa is prolonged.
- The systemic concentration of dopamine is reduced.
- Response to levodopa appears earlier.
- Side effects like nausea and vomiting are reduced.
- Cardiac complications are minimized.
- Pyridoxine does not interfere with the treatment
- The on-Off effect is minimized.
- The degree of improvement may be higher.
Anti-Parkinsonian Drugs Short Answers
Question 1. Is pyridoxine given with levodopa?
Answer:
Pyridoxine is not given with levodopa because.
- Pyridoxine enhances the decarboxylation of levodopa.
- Reduces the drug availability to the CNS.
- This results in the need for greater doses of levodopa for the same desired result
- Thus, pyridoxine is not combined with levodopa.
Anti-Arrhythmic Drugs Important Notes
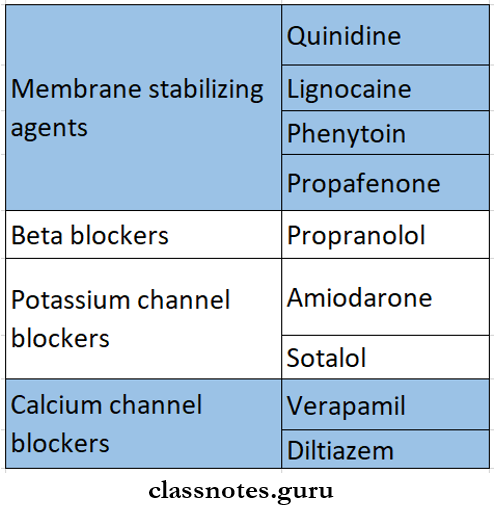
1. Antiarrythmic Drugs Classification
Anti Arrythmic Drugs Short Question And Answers
Question 1. Classification of anti-arrhythmic drugs.
Answer:
Arrhythmic Drugs Classification:
1. Class – 1 – Sodium channel blockers.
- Prolong repolarization – Quinidine, procainamide,
- Shorten repolarization – Lignocaine, mexiletine.
- Little or no repolarization – Propafenone, Flecainide.
2. Class 2 – β blockers.
- Propranolal, esmolol.
3. Class – 3 – Potassium channel blockers.
- Amiodarone, Dofetilide.
4. Class – 4 – Calcium channel blockers.
- Verapamil, diltiazem.
Parkinson’s disease pharmacology MCQs
Question 2. Why procainamide is preferred to procaine?
Answer:
Procainamide is a derivative of procaine.
- It is preferred to procaine because.
- It has weak anticholinergic action.
- Has antiarrhythmic action, while procaine has only a local anesthetic effect
- It is better tolerable.
