Anti Cancer Drugs Important Notes
1. Methotrexate
- It is the folic acid antagonist
- Has antineoplastic activity
- Extensively used as a chemotherapeutic agent
Read And Learn More: Pharmacology Question and Answers
Anti Cancer Drugs Short Essays
Question 1. Toxic effects of alkylating agents.
Answer:
Alkylating agents produce highly reactive carbonium ion intermediates which transfer alkyl groups to cellular macromolecules by forming covalent bonds.
They are:
1. Nitrogen mustards.
- Cyclophosphamide
- Ifosfamide.
- Chlorambucil.
- Melphalan.
2. Alkyl sulfonate-busulfan.
3. Nitrosoureas – lomustine.
4. Triazine – dacarbazine.
Anti cancer drugs short essay questions and answers
Toxic effects of alkylating agents:
1. Bone marrow depression.
- It results in granulocytopenia, agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia, and aplastic anemia.
2. Immunosuppression.
- Lymphocytopenia and inhibition of lymphocyte function result in suppression of immunity.
3. GIT disturbances.
- Stomatitis, diarrhea, shedding of mucosa, and hemorrhages occur.
- Nausea and vomiting are prominent
4. Skin and hair.
- Alopecia – loss of hair and dermatitis occurs.
5. Gonads.
- Inhibition of gonadal cells causes.
- Oligozoospermia and impotence – in males.
- Inhibition of ovulation and amenorrhoea in females.
6. Foetus.
- Damages foetus.
- Leads to abortion, fetal death, and teratogenesis.
7. Carcinogenicity.
- Secondary cancers appear frequently due to immunosuppression.
8. Hyperuricaemia.
- Massive cell destruction produces uric acid.
- Gout and urate stones in the urinary tract may develop.
Question 2. Vinca alkaloids.
Answer:
- Vinca alkaloids are spindle poison.
- They are mitotic inhibitors.
Vinca alkaloids Mechanism of action:
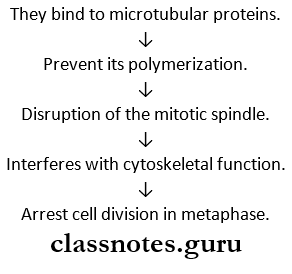
Anticancer drugs pharmacology short notes
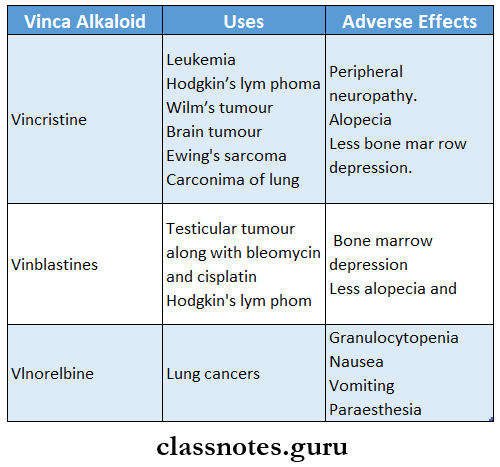
Vinca alkaloids: are
- Vincristine
- Vinblastine
- Vinorelbine.
Question 3. Two antimetabolites are used in cancer therapy.
Answer:
Antimetabolites are analogs related to the normal components of DNA. Involved in nucleic acid synthesis.
- They competitively inhibit the utilization of normal substrate.
1. Folate antagonist – methotrexate.

Folate antagonist- methotrexate Action:
- Cytotoxic actions on bone marrow, skin, gastrointestinal m synthesis.
Folate antagonist- methotrexate Uses:
- Choriocarcinoma.
- Acute leukemia.
- Carcinoma of tongue/pharynx/lung.
- Rheumatoid arthritis.
- Psoriasis.
- Organ transplantation.
Folate antagonist- methotrexate Treatment of toxicity:
- Methotrexate toxicity is treated with folinic acid.
- It reverses the effects of methotrexate.
2. Purine antagonists – mercaptopurine.
Treatment of toxicity mercaptopurine Mechanism of action:
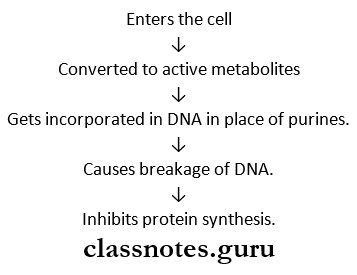
Classification of anticancer drugs short answer
Treatment of toxicity Uses:
- Acute leukemia in children.
- Choriocarcinoma.
- Some solid tumors.
Treatment of toxicity Adverse effects:
- Bone marrow depression.
- Anorexia.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Stomatitis.
- Jaundice.
- Dermatitis.
Question 4. Methods to ameliorate the toxicity of anticancer drugs.
Answer:
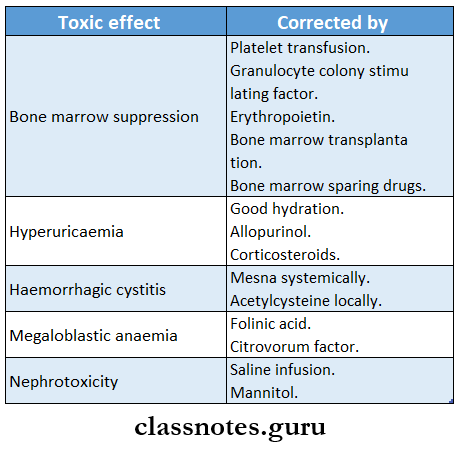
Question 5. Methotrexate.
Answer:
- It is an anticancer drug
- It is a folate antagonist
Methotrexate Mechanism:
- Binds to dihydrofolate reductase
- Prevents the formation of tetrahydrofolate
Methotrexate Action:
- Cytotoxic actions on bone marrow, skin, GIT, and synthesis
Methotrexate Dose:
- Initial 7.5 mg once weekly
- Increased by 2.5 mg weekly
- Maximum weekly dose – 30 mg
Methotrexate Uses:
- Choriocarcinoma
- Acute leukemia
- Carcinoma of tongue/ pharynx/ lung
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Psoriasis
- Organ transplantation
Methotrexate Adverse Effects:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Mucosal ulcers
- Hepatotoxicity
- Treatment of Toxicity:
- Methotrexate toxicity is treated with folinic acid
- It reverses the effects of methotrexate
Cytotoxic drugs short essay for exams
Anti Cancer Drugs Short Question And Answers
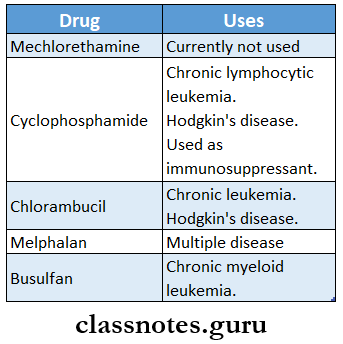
Question 1. Nitrogen mustards.
Answer:
Nitrogen mustards are alkylating agents.
Question 2. Name antibiotics used in cancer therapy.
Answer:
Antibiotics used in cancer therapy are.
- Actinomycin D.
- Daunorubicin.
- Doxorubicin.
- Bleomycin.
Question 3. Name vinca alkaloids.
Answer:
Vinca alkaloids are mitotic inhibitors.
- They are.
- Vincristine
- Vinblastine
- Vinorelbine.
Anticancer drugs mechanism of action essay
Question 4. Antimetabolites.
Answer:
Antimetabolites are analogs related to the normal components of DNA involved in nucleic acid synthesis.
They are:
1. Folate antagonist.
- Methotrexate.
2. Purine antagonist
- Mercaptopurine.
- Thioguanine.
- Azathioprine.
3. Pyrimidine antagonists.
- Fluorouracil.
- Cytarabine.
Anti cancer agents BSc nursing short answer
Question 5. Cyclophosphamide.
Answer:
- Cyclophosphamide is an alkylating agent
- It is converted to its active metabolite aldophosphamide in the body.
- It is more effective on B cells than T cells.
Cyclophosphamide Uses:
- Bone marrow transplantation.
- Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
- Leukemia.
- Maintenance therapy in pemphigus, systemic lupus erythematosus, and idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura.
Cyclophosphamide Toxic effects:
- It causes cystitis due to its active metabolite caroline.
- Prevent by.
- IV mesna.
- Irrigating bladder with acetylcysteine.
- Intake of excessive fluids.
Short note on chemotherapy drugs
Question 6. Oxythiamine.
Answer:
- It is an irreversible inhibitor of transketolase
- It is an antivitamin derivative of thiamine which after phosphorylation to oxy thiamine pyrophosphate can bind to the active centers of thiamine-dependent enzymes
Oxythiamine Action:
- It is analog to antimetabolite
- Suppresses the nonoxidative synthesis of ribose
- Induces cell apoptosis
Oxythiamine Mechanism of Action:
Inhibits transketolase
↓
Suppresses pentose phosphate pathway
↓
Interrupts the synthesis of coenzymes, RNA, and DNA in
cancer cells
