Aids And The Periodontium Important Notes
1. Gingival and periodontal diseases in HIV Linear gingival erythema
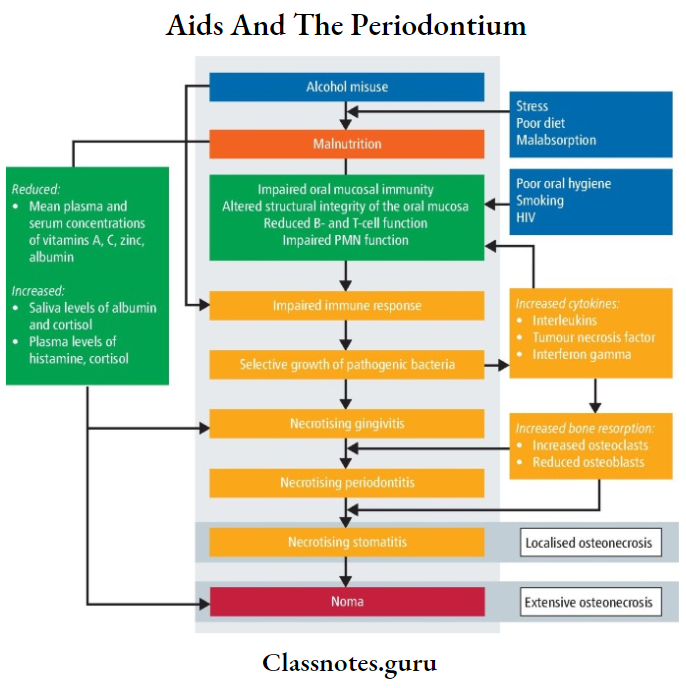
- Necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis
- Necrotizing ulcerative periodontitis
2. Oral hairy leukoplakia
- Primarily occurs in persons with HIV infection
- Found chiefly on the lateral borders of the tongue bilaterally
- The lesions do not rub off and resemble other keratotic oral lesions
Read And Learn More: Periodontics Question and Answers
Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis Short Essays
Question 1. HIV periodontitis.
Answer:
1. HIV-associated gingivitis:
- Linear inflammation around the gingival margin occurs
- Presence of punctuate erythema
- The lesion extends throughout the width of the attached gingiva
- This occurs even in the presence of excellent oral hygiene
2. HIV-associated periodontitis:
- Rapid loss of attachment
- Tissue destruction
- Deep pain
3. HIV necrotizing gingivitis:
- Sudden onset
- Bleeding on toothbrushing
- Pain
- Characteristic halitosis
- Gingiva appears fairly red and swollen
- Presence of yellow to grayish necrosis
- Common in anterior gingival
4. Necrotizing stomatitis:
- Sequestration of interdental bone
- Soft tissue necrosis
- It is the most severe form of periodontal infection
Question 2. Oral manifestations of AIDS.
Answer:
Oral Manifestations Of Aids:
1. Oral hairy leukoplakia:
- Found on lateral borders of the tongue
- Caused by human papillomavirus
- Keratotic, asymptomatic area with vertical stria- tions giving a corrugated appearance
- When dried appears hairy
2. Oral candidiasis:
- Manifested as
- Pseudomembranous candidiasis
- Erythematous candidiasis
- Hyperplastic candidiasis
- Angular chelitis
3. Kaposi’s sarcoma:
- Multifocal, vascular neoplasm manifested as nodules, papules, or non-elevated macules
4. Bacillary angiomatosis:
- It is an infectious vascular proliferative disease
- It appears red, purple, or blue edematous soft tissue lesion
5. Oral hyperpigmentation
6. Atypical ulcers and delayed healing
Aids And The Periodontium Short Question and Answers
Question 1. Periodontal disease associated with HIV.
Answer:
1. HIV-associated gingivitis (HIV-G):
- Linear inflammation around the gingival margin
- Punctuate erythema
2. HIV-associated periodontitis (HIV-P):
- Rapid loss of attachment
- Tissue destruction
- Deep pain
3. HIV- necrotizing gingivitis (HIV-NG) – ANUG:
4. Necrotizing stomatitis (NS):
- Sequestration of interdental bone
- Soft tissue necrosis
Question 2. Tests for HIV
Answer:
1. ELISA(Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay):
- It is a color reaction test
ELISA Method:
- A serum containing antibodies is developed from the patient’s blood sample
- It is added to the ELISA plate
- Wash off the inactive antibodies
- A second layer of antibodies called conjugate is added
- Excess antibodies are again washed off
- A substrate is added to it
ELISA Result:
- Color becomes darker- positive test
- No color change- negative test
2. Western blot test:
Western Blot Test Method:
- Viral proteins from the patient’s blood sample are passed through a gel
- The separated proteins are then passed through an electric current
- Human serum is added
- A chromogen is added to it
Western Blot Test Result:
- A specific band of viral protein is detected
Question 3. Linear Gingivitis.
Answer:
Linear Gingivitis:
- Color – Bright red
- Site – Marginal and attached gingiva
- Bleeding on probing – present
- Progression – Involves entire gingiva
Linear Gingivitis Negative Features:
- No ulceration
- No attachment loss
- No response to treatment
- No relation with plaque accumulation
Linear Gingivitis Treatment:
- Medical consultation
- Scaling
- Irrigation with 10% povidone-iodine
- Mouth rinse-0.12% chlorhexidine Antifungal agents
- daily
Linear Gingivitis Recalls:
- Next day
- After one week
- Every 4 weeks
- Every 3-6 months
Aids And The Periodontium Viva Voce
- Candidiasis is found in 90% of AIDS patients
- In linear gingival erythema, the erythematous, easily bleeding gingiva may be limited to marginal gingiva or may be diffuse extending into attached gingiva
- CD4+ T lymphocyte levels less than 200/mm3 are definitive for AIDS and indicate severe immunogenic- science
