Aggressive Periodontitis
Aggressive Periodontitis Important Notes
1. Signs of aggressive periodontitis
- Mobility
- Pathological migration of first molars and incisors
- Distolabial migration of maxillary incisors with diastema formation
- Lack of inflammation
- Presence of deep periodontal pockets
2. Aggressive periodontitis is differentiated from chronic periodontitis by
- Age of onset
- The rapid rate of disease progression
- Nature and composition of the associated subgingival microflora
- Alterations in the host’s immune response
- Familial aggregation of diseased individuals
- Racial influence
Read And Learn More: Periodontics Question and Answers
3. Periodontal diseases associated with neutrophils disorder
- Aug
- Localized juvenile periodontitis
- Various forms of aggressive periodontitis
4. Types of juvenile periodontitis
- Localized
- Characterized by a distribution of lesions in the first molars and incisors with the least destruction in the cuspid-premolar
- Generalized
- There is generalized involvement of teeth
5. Juvenile periodontitis
- Also known as periodontosis
- Microflora are composed of gram-negative bacteria, including cocci, rods, filaments, and spirochaetes
- Microbes identified are
- Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans
- Capnocytophaga
- Mycoplasma and spirochaetes
Aggressive Periodontitis Long Essays
Question 1. Describe clinical features, diagnosis, and management of localized juvenile periodontitis. (or) Describe the etiology, clinical features, and treatment of localized aggressive periodontitis.
Answer:
Localized Aggressive Periodontitis:
Rapid loss of attachment and bone loss occurring in an otherwise clinically healthy patient with the number of microbial deposits inconsistent with disease severity and familial aggregation of diseased individuals
Localized Aggressive Periodontitis Clinical Features:
- Age- 20 years
- Sex- common in females
- The site involves incisors and the first molar
- Lack of inflammation
- Deep pockets
- A small amount of plaque
- Mobility of first molars and incisors
- Midline diastema
- Root sensitivity
- Deep dull radiating pain
- Periodontal abscess
- Lymphadenitis
Localized Aggressive Periodontitis Radiographic Features:
- Vertical/ angular bone loss
- Arc-shaped loss of alveolar bone extending from distal surface of 2nd premolar to mesial surface of 2nd molar
- Bilateral involvement results in a “mirror image” pattern
Localized Aggressive Periodontitis Treatment:
- Extraction of 1st molar and transplantation of 3rd molar in its position
- Scaling and root planning
- Curettage
- Root amputation
- Hemisection
- Antibiotic therapy
- Tetracycline-250 mg QID for 14 days Doxycycline-100 mg/day
- Chlorhexidine rinses
Question 2. Define and classify plaque. Describe the plaque-host interaction in juvenile periodontitis.
Answer:
Plaque Definition:
- Plaque is soft deposits that form biofilm adhering to the tooth surface or other hard surfaces in the oral cavity including removable and fixed restoration
Plaque Classification:
- Dental plaque is classified into
- Supragingival plaque
- Subgingival plaque
- It is further divided into
- Tooth associated
- Epithelium associated
Plaque-Host Interaction:

Aggressive Periodontitis Short Essays
Question 1. Aggressive Periodontitis.
Answer:
Aggressive Periodontitis Definition:
- Rapid loss of attachment and bone loss occurs in an otherwise clinically healthy patient with the number of microbial deposits inconsistent with disease severity and familial aggregation of diseased individuals.
Aggressive Periodontitis Types:
- Localized Aggressive Periodontitis
- Generalized Aggressive Periodontitis
Aggressive Periodontitis Microbiology:
- A.actinomycetem contains
- Capnocytophaga
Aggressive Periodontitis Virulence Factors:
- Leukotoxin – Destroys leukocytes
- Endotoxins – Activates host cells
- Secretes inflammatory mediators
- Bacteriocin – Inhibit IgG and IgM production
- Collagenase-Degradation of collagen
- Chemotactic Inhibiting factors Inhibit neutrophil chemotaxis
Aggressive Periodontitis Risk Factors:
- Microbiologic Factors – A.a.comitans
- Immunologic Factors – Neutrophil defect
- Genetic factors
- Environmental factors – Smoking
Question 2. Localized Aggressive Periodontitis (LAP).
Answer:
Localized Aggressive Periodontitis Clinical Features:
- Age – 20 years
- Sex – common in females
- The site involves – Incisors and the first molar
Localized Aggressive Periodontitis Reason-Production Of Antibodies:
- Bacteria antagonist
- Losing of leukotoxin-producing ability
- Defect in cementum formation
Localized Aggressive Periodontitis Associated Features:
- Lack of inflammation
- Deep pockets
- A small amount of plaque
- Mobility of first molars and incisors
- Midline diastema
- Root sensitivity
- Deep dull radiating pain
- Periodontal abscess formation
- Lymphadenitis
Localized Aggressive Periodontitis Radiographic Features
- Vertical/Angular bone loss
- Arc-shaped loss of alveolar bone extending from distal surface of 2nd premolar to mesial surface of 2nd molar
Localized Aggressive Periodontitis Microbiology:
- A.a. contains
- Capnocytophaga
Localized Aggressive Periodontitis Treatment Modalities:
- Extraction of 1st molar and transplantation of 3rd molar in its position
- Scaling and root planning
- Curettage
- Root amputation
- Hemisection
- Antibiotic therapy
- Tetracycline 250 mg QID for 14 days
- Doxycycline 100 mg/day
- Chlorhexidine rinses
Question 3. Generalized Aggressive Periodontitis.
Answer:
Characterized by generalized interproximal attachment loss affecting at least three permanent teeth other than first molars and incisors
Microbiology:
- P.gingivalis
- A.actinomycetem contains
- Bacteroids forsythias
Gingival Response:
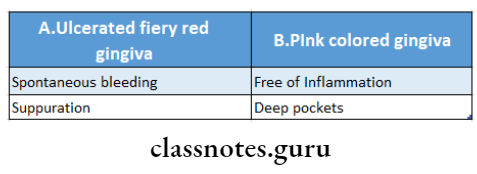
Generalized Aggressive Periodontitis Features:
- Weight loss
- Mental depression
- General malaise
Generalized Aggressive Periodontitis Clinical Features:
- Age Between puberty and 35 years
- Sex-both sex
Aggressive Periodontitis Short Question and Answers
Question 1. Define Aggressive Periodontitis/Juvenile Periodontitis.
Answer:
Rapid loss of attachment and bone loss occurs in an otherwise clinically healthy patient with the number of microbial deposits inconsistent with disease severity and familial aggregation of diseased individuals.
Question 2. Microbiologic of LAP.
Answer:
- Causative organisms of LAP are
- A.a. contains
- Capnocytophaga
Question 3. Risk factors for Aggressive Periodontitis.
Answer:
Aggressive Periodontitis Risk Factors
- Microbiologic factors- A.a. contains
- Immunologic factors- Neutrophil defect
- Genetic factor
- Environmental factors-smoking
Question 4. Virulence factors.
Answer:
Virulence Factors:
- Leukotoxin- Destroys leukocytes
- Endotoxin
- Activates host cells
- Secretes inflammatory mediators
- Bacteriocin- Inhibits IgG and IgM production
- Collagenase- degrades collagen
- Chemotactic inhibiting factors- inhibits neutrophil chemotaxis
Question 5. Stages in Development of Disease.
Answer:
Development of Disease Stage 1:
- Degeneration of principal fibers
- Cessation of cementum formation
- Bone resorption
- Absence of inflammation
- Tooth migration
Development of Disease Stage 2:
- Loss of periodontal fibers
- The rapid proliferation of JE
- Initiation of inflammation
Development of Disease Stage 3:
- Progressive inflammation
- Deep, infra bony pockets
Question 6. Burn-out Phenomenon.
Answer:
- Concept explaining localization of aggressive periodontitis
- Localized aggressive periodontitis is confined to incisors and first molars
- Micro-organisms responsible for it A.a. contains
- The reason for localization is the production of opsonizing antibodies against it.
Question 7. Radiographic features of LAP.
Answer:
- Vertical/Angular bone loss
- Arc-shaped loss of alveolar bone extending from distal surface of 2nd premolar to mesial surface of 2nd molar
- Bilateral involvement results in a “mirror image” pattern
Question 8. Differences between localized and generalized aggressive periodontitis.
Answer:
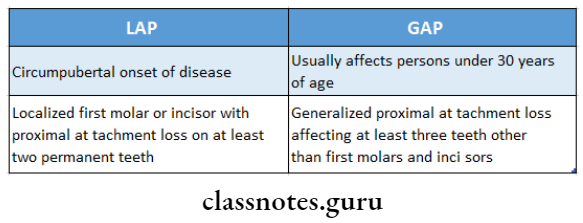
Aggressive Periodontitis Viva Voce
- Periodontosis is the old name for juvenile periodontist- tis or aggressive periodontitis
- Gingivosis is the old name for desquamative gingivitis
- Vertical bone loss around incisors and molars is diag- nostic of localized juvenile periodontitis
- Arc-shaped bone loss extending from the distal surface of the second premolar to the mesial surface of the second molar creating a mirror image is characteristic of juvenile periodontitis
