Adrenergic System Important Notes
1. Adrenergic System Adrenergic receptors
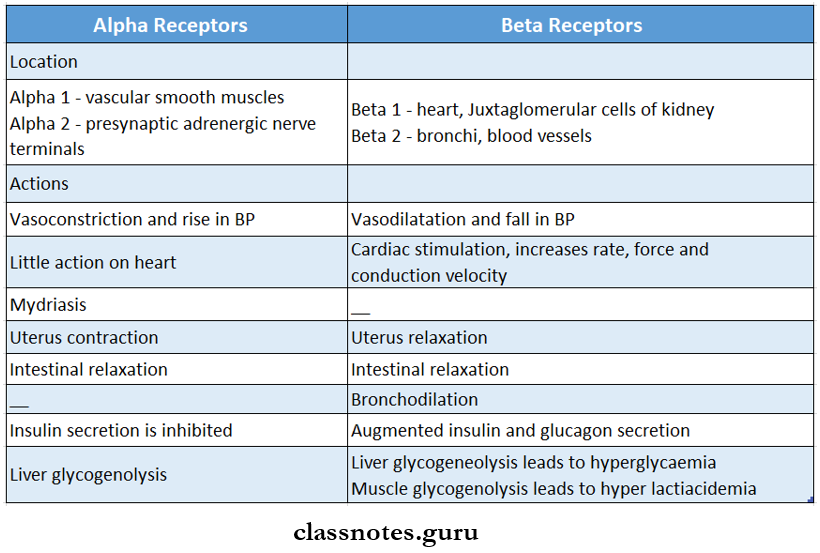
- They are present at the post-ganglionic sympathetic nerve endings
- Types are: alpha and beta receptors
Read And Learn More: Pharmacology Question and Answers
2. Adrenergic System Adrenergic Drugs
Adrenergic drugs pharmacology
3. Adrenergic System Adrenaline
- Acts on both alpha and beta receptors but predominantly on beta
- It increases heart rate, the force of contraction, cardiac output, and oxygen consumption
- On IV administration there is an initial rise in BP due to stimulation of alpha receptors, later there is a fall in BP due to the effect of beta receptors
4. Adrenergic System Uses of adrenaline
- In syncopal attacks
- For resuscitation of a failing heart
- In allergic disorders
- As bronchodilators
- To prolong the effect of local anesthesia
- To control hemorrhage by producing vasoconstrictor
Alpha 2 Adrenergic
5. Adrenergic System Isoprenaline
- It has a selective beta receptor stimulant effect
- It stimulates myocardium
- Produces vasodilatation
- Relaxes smooth muscles of bronchi and GFT
- Mainly used as
- Bronchodilator
- The cardiac stimulant in heart block
6. Adrenergic System Dopamine
- It is the precursor of noradrenaline
- Acts on both alpha and beta receptor
- Acts on dopamine receptors in the mesenteric and vascular beds
- Used in the treatment of cardiogenic shock
Alpha 2 Adrenergic
7. Adrenergic System Non catecholamines
Adrenergic System Long Essays
Question 1. Discuss pharmacological actions and some important uses of sympathomimetic drugs.
(or)
Classify sympathomimetics and write the therapeutic uses, pharmacological action, and adverse effects of adrenaline.
(or)
Classify adrenergic agents. Discuss the action and uses of adrenaline.
Answer:
Sympathomimetics/Adrenergic drugs:
These are drugs with action similar to that of adrena¬line or sympathetic stimulation.
Alpha 2 Adrenergic
Sympathomimetics Classification:
1. Sympathomimetics Based on mode of action:
- Direct-acting sympathomimetic.
- They act directly on a and/or b adrenoreceptors.
- Example: adrenaline, noradrenaline, and isoprenaline.
- Indirect-acting sympathomimetic.
- They act on adrenergic neurons to release noradrenaline which then acts on adrenoreceptors
- Example: Tyramine.
- Mixed action was sympathomimetic.
- They act directly as well as indirectly.
- Example: ephedrine, dopamine.
2. Sympathomimetics Based on chemical structure.
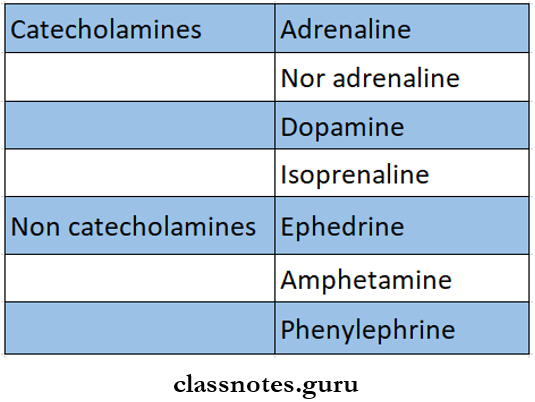
- Catecholamines – contain – a catechol nucleus.
- Example: Adrenaline, noradrenaline, dopamine.
- Non-catecholamines – lack catechol nucleus.
- Example: Ephedrine. amphetamine, tyramine.
Adrenergic system questions
3. Sympathomimetics Based on therapeutic use.
- Vasopressor – raises blood pressure.
- Example: Noradrenaline – phenylephrine, ephedrine.
- Cardiac stimulants – Adrenaline, dopamine.
- CNS stimulants – Amphetamine, ephedrine.
- Bronchodilators. Adrenaline, salbutamol.
- Nasal decongestants – phenylephrine, ephedrine.
- Anorectic – fenfluramine.
- Uterine relaxants – salbultamol, terbutaline.
Adrenaline:
Adrenaline Pharmacological action:
1. Adrenaline Cardiovascular system.
- Heart
- Adrenaline is a powerful cardiac stimulant
- It increases.
- Heart rate
- Force of contraction
- Oxygen consumption.
- Conduction
- Cardiac output
- Blood vessels and blood pressure.
- Vasoconstriction of vessels of the skin and mucous membrane occurs.
- It constricts renal, mesenteric, pulmonary, and splanchnic vessels.
- It dilates blood vessels of skeletal muscles and coronary vessels.
- It causes an initial rapid increase in BP followed by a fall. This is called a biphasic response.
2. Adrenaline Respiratory system.
- Adrenaline is a powerful bronchodilator.
- It is a weak respiratory stimulant
- Inhibits release of inflammatory mediators.
- Reduces secretions.
3. Adrenaline GIT
- Causes gut relaxation, decreases motility, and constricts the sphincter.
4. Adrenaline Bladder.
- Causes relaxation of the detrusor muscle and contraction of the trigone sphincter.
5. Contraction of hair follicles.
6. Adrenaline Eye.
- Adrenaline penetrates the cornea poorly.
7. Adrenaline Uterus.
- Contracts non-pregnant uterus and relaxes during the last month of pregnancy.
8. Adrenaline CNS
- Does not cross the BBB
- Activation of aa receptors in the brainstem results in decreased sympathetic outflow.
9. Adrenaline Metabolic
- Produces glycogenolysis, lipolysis, calorignesis, and transient hyperkalemia.
10. Adrenaline Skeletal muscle.
- Facilitates neuromuscular transmission.
Adrenaline Uses:
Adrenaline Adverse Effects:
- CVS effects – tachycardia, palpitation, rise in BP, cardiac arrhythmias.
- CNS effects – tremors, anxiety, throbbing headache.
- Respiratory effects include acute pulmonary edema.
- Others – pillar, dizziness, weakness, restlessness.
- Metabolic effects – hyperglycemia, hyperlactatemia, and hypokalaemia.
Question 2. Write all uses of adrenaline and isoprenaline.
Answer:
Uses of Adrenaline:
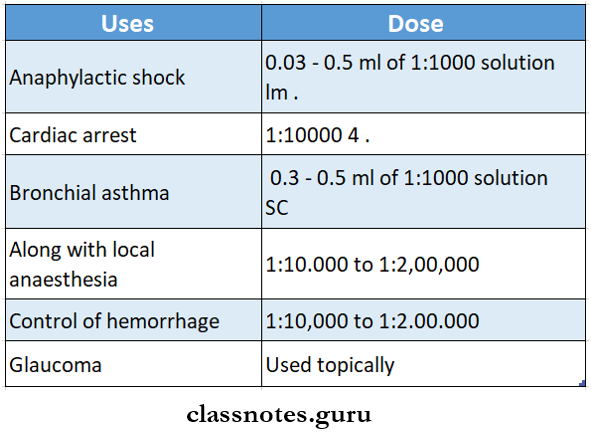
1. Adrenaline In anaphylactic shock.
- Adrenaline 0.3 – 0.5 ml of 1:1000 solution is given subcutaneously.
- It reverses hypotension, laryngeal edema, and bronchospasm.
2. Adrenaline Cardiac arrest.
- Intracardiac adrenaline into the 4th or 5th intercostal space, 2-3 inches from the sternum, is given in cardiac arrest.
3. Adrenaline Control of Hemorrhage.
- Cotton or gauze soaked in adrenaline, 1:10,000 to 1:20,000 concentration, is used.
4. Adrenaline used along with local anesthesia (LA)
- 1:10,000 to 1:2,00,0000 adrenaline is used
- It produces vasoconstriction and reduces the rate of absorption of LA.
5. Adrenaline Bronchial asthma.
- Adrenaline produces bronchodilation.
- 0.3 – 0.5 ml of a 1:1000 solution of SC is used.
6. Adrenaline Glaucoma.
- Adrenaline reduces intraocular pressure.
- It is used topically
7. Allergic reactions.
Uses of isoprenaline:
- Used as a cardiac stimulant in heart block and shock.
- Used in bronchial asthma.
- Used as a temporary measure to maintain a sufficient ventricular rate.
Adrenergic receptors
Question 3. Describe the differences in the action of adrenaline, noradrenaline, and isoprenaline. Write their uses, indicating the route of administration and usage.
Answer:
Adrenaline, noradrenaline, and isoprenaline are sympathomimetic drugs.
- Their actions are mediated by α and β receptors.
Adrenaline – Has α1, α2, β1, and β2 actions
Noradrenaline – Has α1, α2, β1 but no β2 action
Isoprenaline – Has β1 and β2 but no actions
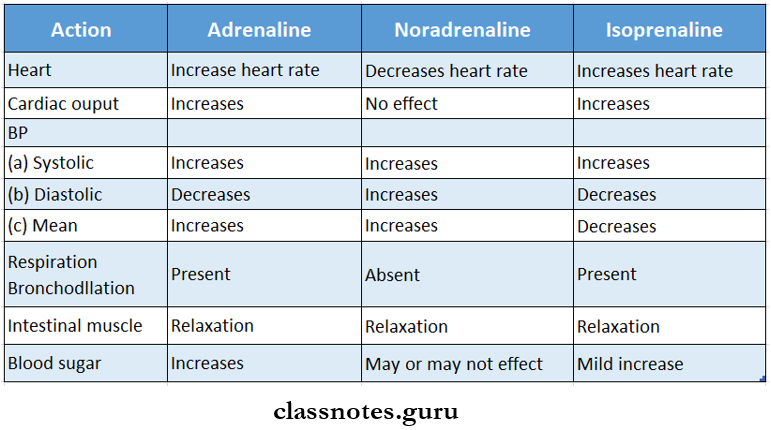
Uses Of Noradrenaline
- It is rarely used in shock to increase BP.
- 8 mg in 100 – 200 ml saline is used to control local bleeding from the skin and mucous membranes.
Routes Of Administration
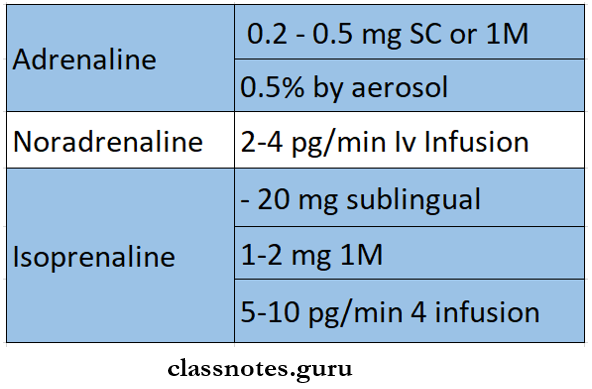
Adrenergic System Short Essays
Question 1. Compare adrenaline and ephedrine.
Answer:
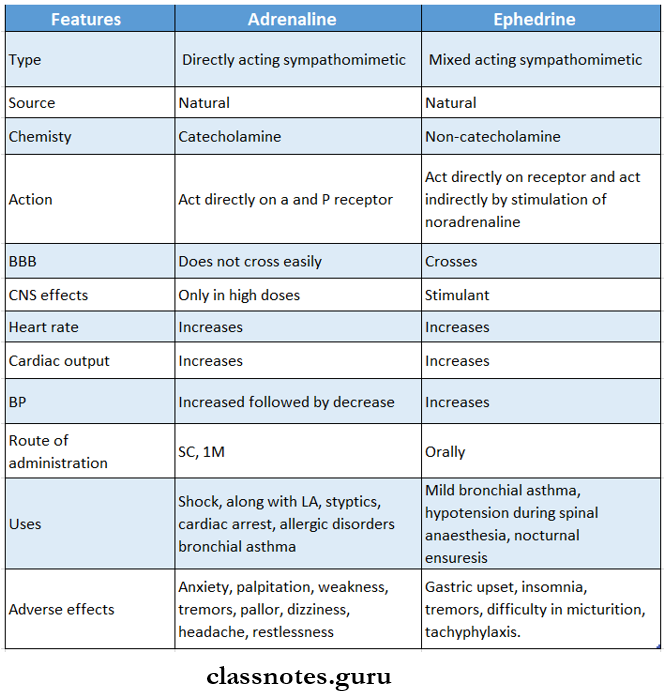
Question 2. Compare adrenaline and noradrenaline.
Answer:
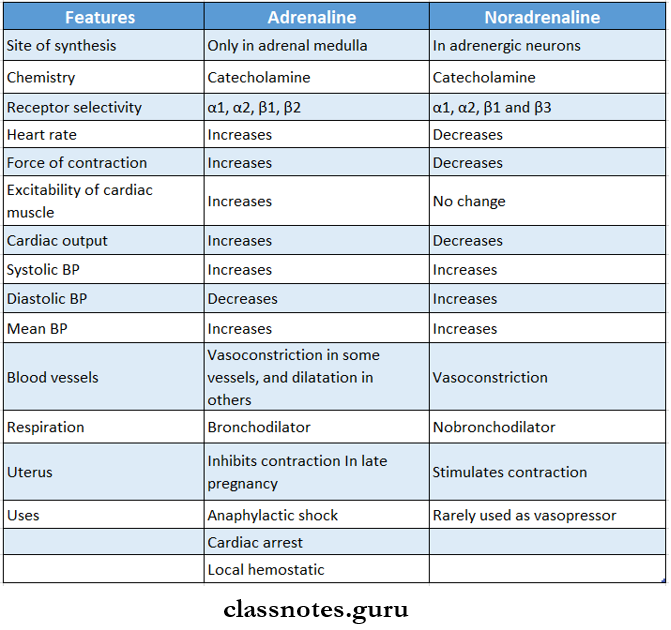
Question 3. Dopamine
Answer:
It is a catecholamine and the immediate precursor of noradrenaline.
- It is a central neurotransmitter.
- It acts on dopaminergic and adrenergic receptors.
Dopamine Actions:
1. Dopamine at low doses.
- Stimulates vascular D1 receptors in renal, mesenteric, and coronary beds.
- Causes vasodilatation of these vessels.
- Results in increases in renal blood flow, GFR, and Na+ excretion.
2. Dopamine at moderate doses.
- Produces positive ionotropic effects.
3. Dopamine: At high doses.
- Causes cardiac stimulation.
- Results in vasoconstriction and increased BP.
4. Dopamine CNS
- Does not cross the BBB.
Dopamine Uses:
- In cardiogenic, hypovolemic, and septic shock.
- In severe heart failure with renal impairment.
Dopamine Adverse Effects:
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Headache, palpitation.
- Angina, hypertension, tachycardia.
Dopamine Dose:
- 2 – 5 pg/kg/min 4
Question 4. Uses of Adrenaline with rationale and route of administration.
Answer:
Uses Of Adrenaline:
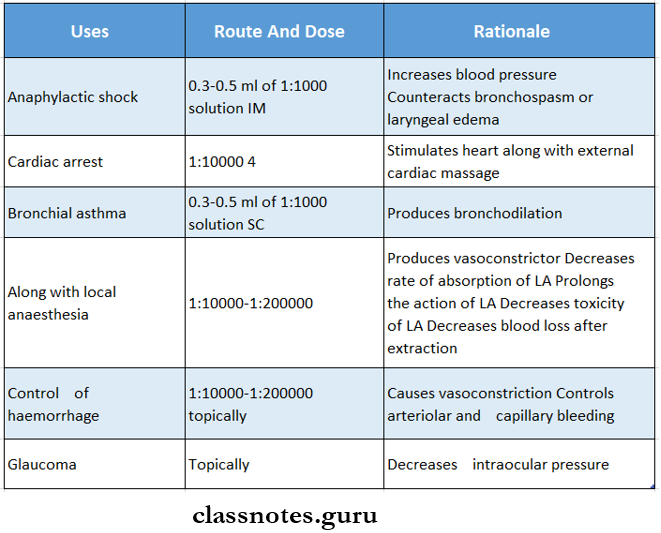
Question 5. Beta 2 agonists.
Answer:
- Beta 2 agonists are drugs that act on β2 adrenergic receptors
Beta 2 agonists: Mechanism of Action:
β2 are coupled to the stimulatory G protein of adenylyl cyclase
↓
Produces cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP)
↓
cAMP decreases calcium concentration in cells
↓
This leads to smooth muscle relaxation and bronchodilation
Beta 2 agonists Actions:
- Smooth muscle relaxation
- Bronchodilation
- Vasodilation in the muscle and liver
- Relaxation of the uterine muscle
- Release of insulin
Beta 2 agonists Classification:
- Short acting – fenoterol, isoprenaline, salbutamol, Terbutaline
- Long acting – bambuterol, formoterol, salmeterol
- Ultra long-acting-abediterol, formoterol, olodaterol
Beta 2 agonists Uses:
- Bronchial asthma
- COPD
Beta 2 agonists: Adverse Effects:
- Tachycardia
- Palpitation
- Tremor
- Excessive sweating
- Anxiety
- Insomnia
- Agitation
Adrenergic agonists and antagonists
Adrenergic System Short Answers
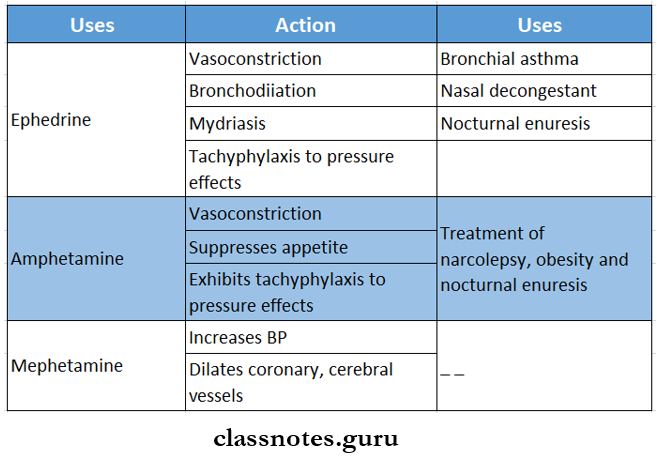
Question 1. Ephedrine.
Answer:
Ephedrine is an alkaloid obtained from the plant of the genus Ephedra vulgaris.
Ephedrine Mechanism:
- Act directly on α and β receptors.
- Act indirectly by the release of noradrenaline.
Ephedrine Actions:
- Crosses BBB and causes stimulation.
- Increases BP
- Vasoconstriction.
- Increases cardiac output
- Relaxation of smooth muscles.
- Bronchodilator.
Ephedrine Uses:
- Effective orally
- Mild bronchial asthma.
- As a nasal decongestant
- For hypotension during spinal anesthesia.
- Produces mydriasis.
- Used in narcolepsy and nocturnal enuresis.
Ephedrine Adverse Effects:
- Gastric upset, difficulty in micturition.
- Repeated injections cause tachyphylaxis.
- Insomnia, tremors.
Question 2. Amphetamine.
Answer:
Amphetamine is a synthetic compound.
- It is effective orally.
- It has a long duration of action.
Amphetamine Actions:
1. CNS – stimulant
- Includes alertness, increased concentration, euphoria, talkativeness, and increased work capacity.
- Improves athletic performance.
- The effect is temporary.
2. Respiration.
- Stimulates respiratory centers.
3. Suppression of appetite.
Amphetamine Adverse Effects:
- Drug dependence.
- High doses caused delirium, hallucinations, and an acute psychotic state.
- Long-lasting behavioral abnormalities.
- Develops psychosis.
Question 3. The rationale of using xylocaine with adrenaline for local anesthesia.
Answer:
Adrenaline is combined with xylocaine for local anaes¬thesia because adrenaline causes.
- Vasoconstriction.
- Reduces the rate of absorption of local anesthesia
- Prolongs its action.
- Reduces blood loss after extraction.
- Decreases toxicity.
Adrenergic neurotransmitters
Question 4. The rationale for using adrenaline in anaphylactic shock.
Answer:
0.3 – 0.5 ml of a 1:1000 solution of adrenaline is used IM in anaphylactic shock because.
- Adrenaline is an antagonist of histamine, the mediator of anaphylactic shock.
- Increases BP.
- Reverse bronchospasm or laryngeal edema.
Question 5. The rationale for using dopamine in shock.
Answer:
Dopamine is used in shock because.
- It dilates renal, mesenteric, and coronary blood vessels.
- Increases renal blood flow, GFR, Na+ secretion
- Improves blood flow to vital organs.
- Increases blood pressure and causes urine outflow
- Stimulates the heart and increases the forces of contraction and cardiac output.
Adrenergic system notes
Question 6. Noradrenaline.
Answer:
Noradrenaline is a catecholamine.
- It acts on α1, α2, β1, and β3 receptors.
Noradrenaline Actions:
- Increases systolic, diastolic, and mean BP.
- Decreases heart rate and force of contraction.
- Causes vasoconstriction.
- Stimulates contraction of the uterus.
Noradrenaline Uses:
- Rarely used as a vasopressor.
