Adrenergic Antagonist Important Notes
1. Sympathetic blocking drugs
2. Uses of alpha-blockers
- Pheochromocytoma
- Hypertension
- Peripheral vascular diseases
- Congestive cardiac failure
- Benign hypertrophy of the prostate
Read And Learn More: Pharmacology Question and Answers
3. Abrupt withdrawal of beta-blocker after chronic use causes
- Rebound hypertension
- Worsening of angina
- Sudden death
Beta 2 Adrenergic Antagonist
Adrenergic Antagonists Pharmacology
Adrenergic Antagonist Long Essays
Question 1. Classify beta-adrenergic receptor blockers. Describe the pharmacological actions, uses and adverse effects of propranolol.
Answer:
Beta-adrenergic receptor blockers:
β-blockers are drugs that block the actions of catecholamines mediated through β -receptors.
Beta-Adrenergic Receptor Blockers Classification:
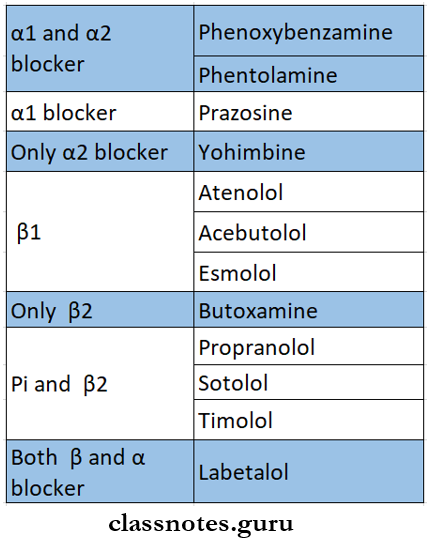
1. Nonselective
- Without intrinsic sympathomimetic activity
- Propranolol, sotalol, timolol.
- With intrinsic sympathomimetic activity
- Pindolol, oxprenolol
- With additional blocking property.
- Labetalol, carvedilol.
Beta 2 Adrenergic Antagonist
2. Cardioselective
- Metoprolol, atenolol, bisoprolol, esmolol, betaxolol
- Propranolol-Propranolol is a first-generation non-selective β-blocker with intrinsic sympathomimetic activity.
Pharmacological actions:
1. CVS:
- Decreases heart rate, force of contraction and cardiac output.
- Decreases BP.
- Cardiac work and oxygen consumption are reduced.
- AV conduction is delayed
- Blocks cardiac stimulant action of adrenergic drugs.
- Improves exercise tolerance in angina patients.
2. Blood vessels.
- Blocks vasodilation produced by isoprenaline.
3. Respiratory tract
- Blocks β2 receptors in bronchial smooth muscles
- Increases bronchial resistance.
4. CNS.
Mild central effects like behavioural changes, forgetfulness, increased dreaming and nightmares occur.
5. Local anaesthetic.
- Potent anaesthetic agent but not used due to irritation.
Beta 2 Adrenergic Antagonist
6. Eye:
- Reduces intraocular pressure.
- Decreases secretion of aqueous humour.
7. Metabolic:
- Blocks adrenergic ally-induced lipolysis.
- Inhibits glycogenolysis.
8. Sekeletal muscle.
- Inhibits adrenergic ally-provoked tremors.
B Adrenergic Antagonist
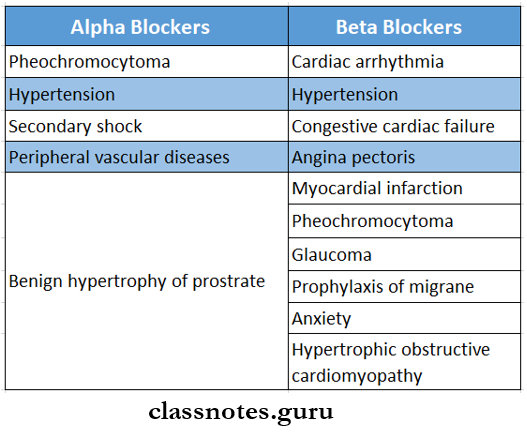
Beta-Adrenergic Receptor Blockers Uses:
- Hypertension
- Prophylaxis of exertional angina.
- Congestive cardiac failure.
- Dissecting aortic aneurysm.
- Cardiac arrhythmia.
- Myocardial infraction.
- Pheochromocytoma.
- Prophylaxis of migrane.
- Glaucoma.
- Anxiety.
- Essential tremor.
- Hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy.
Beta-Adrenergic Receptor Blockers Adverse effects:
- Hypotension.
- Impairment of myocardial function.
- Cold extremities.
- Precipitate acute asthmatic attacks
- Fatigue, weakness.
- Abrupt withdrawal causes rebound hypertension.
- Impairment of carbohydrate tolerance.
B Adrenergic Antagonist
Adrenergic antagonists MCQs
Adrenergic Antagonist Short Essays
Question 1. Adrenergic alpha-blockers.
Answer:
Adrenergic alpha-blockers are drugs that block the adrenergic responses mediated through alpha-adrenergic receptors.
Adrenergic alpha-blockers Classification:
1. Non-equilibrium.
- Phenoxybenzamine.
2. Equilibrium or competitive.
- Non-selective.
- Ergot alkaloids – ergotamine, ergotoxine.
- Hydrogenated ergot alkaloids – dihydro- ergotamine.
- Imidazolines – tolazoline.
- Miscellaneous – chlorpromazine
- α1- selective.
- Prazosin, Terazosin, Doxazosin.
- α2 – selective. – yohimbine.
Adrenergic alpha-blockers Actions:
- Inhibits vasoconstriction, leads to vasodilatation and decreases BP.
- Enhances release of noradrenaline by α2 blocked
- Reflex tachycardia.
- Nasal stiffness and miosis.
- Increased intestinal motility.
- Reduced tone of smooth muscle.
Adrenergic alpha-blockers Uses:
- Pheochromocytoma.
- Hypertension.
- Secondary shock.
- Peripheral vascular diseases.
- Benign hypertrophy of the prostate.
Adrenergic alpha-blockers Adverse effects:
- Postural hypotension, palpitation.
- Nasal stiffness, miosis.
- Impaired ejaculation.
- Impotence.
Adrenergic blockers classification
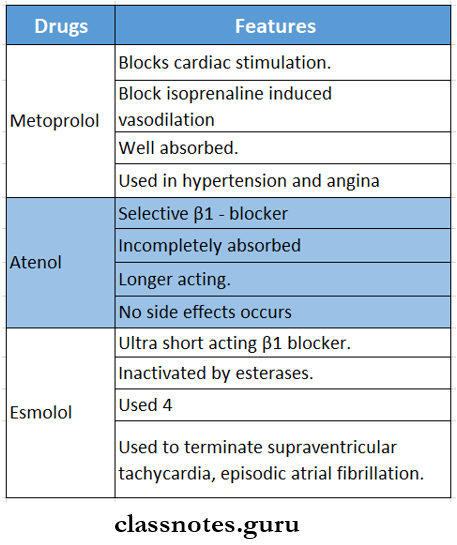
Question 2. Cardioselective beta blockers.
Answer:
Cardioselective beta blockers Actions:
- Selectively block β1 receptors.
- Bronchospasm is less or negligible.
- Less interference with carbohydrate metabolism.
- Lower incidence of cold extremities.
- Impaired exercise performance.
- Lesser chances of peripheral vascular disease.
Drugs included in it:
Adrenergic Antagonist Short Answers
Question 1. Uses of alpha and beta blockers.
Answer:
Alpha 2 Adrenergic Antagonist
Question 2. Prazosin.
Answer:
It is a potent highly selective α1 blocker
Prazosin Actions:
- Blocks sympathetically mediated vasoconstriction.
- Causes fall in BP.
- Dilates arterioles more than veins which result in decreased peripheral vascular resistance and cardiac output
Prazosin Uses:
- Hypertension.
- Left ventricular failure.
- Raynaud’s disease.
- Prostatic hypertrophy.
- Improve urine flow thereby reducing residual urine in the bladder.
Adrenergic antagonists mechanism of action
Question 3. Timolol.
Answer:
- It is a non-selective β blocker.
- It is short acting.
- Orally it is a potent β – blocker.
- Its ocular hypotensive action is smooth and well-sustained.
Timolol Uses:
1. Topically.
- In the treatment of glaucoma.
2. Orally.
- Hypertension.
- Angina
- Prophylaxis of myocardial infarction.
Alpha 2 Adrenergic Antagonist
Question 4. Name cardioselective p blockers.
Answer:
- Cardioselective beta blockers:
- Metoprolol – bisoprolol – celiprolol
- Atenolol esmolol – nebivolol.
- Acebutolol – betaxolol.
Question 5. Propranolol is contraindicated in bronchial asthma Why?
Answer:
- Blockade of β2 receptors of smooth muscles by propranolol causes.
- Increases in airway resistance.
- Precipitation of acute attacks in asthmatics.
- Worsens chronic obstructive lung diseases.
- Thus, it is contraindicated in bronchial asthma.
Adrenergic antagonists short notes
Question 6. Labetalol.
Answer:
Labetalol is the first adrenergic antagonist capable of blocking both α and β receptors.
- It is effective orally.
Labetalol Actions:
- Vasodilation
- Fall in BP
- Reduction in cardiac output, heart rate, and peripheral vascular resistance.
Alpha 2 Adrenergic Antagonist
Labetalol Uses:
- Pheochromocytoma.
- Clonidine withdrawal.
- Essential hypertension.
Labetalol Adverse effects:
- Postural hypotension.
- GI disturbances.
Viva Voce:
Beta-blocker is contraindicated in asthmatic patients
